Present Participle
Related Pages
Present Perfect Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Simple Past Tense
Past Participle
IELTS, TOEFL And English As A Second Language
More Lessons On English Grammar
In this lesson, we will learn
- how to form the present participle?
- when to use the present participle?
- some spelling rules for the present participle
- some examples of present particles used as adjectives
- the differences between the past tense, past participle and present participle.
Present Participle
The present participle is a form of a verb that typically ends in -ing. It’s a versatile part of speech in English, capable of functioning in several ways within a sentence.
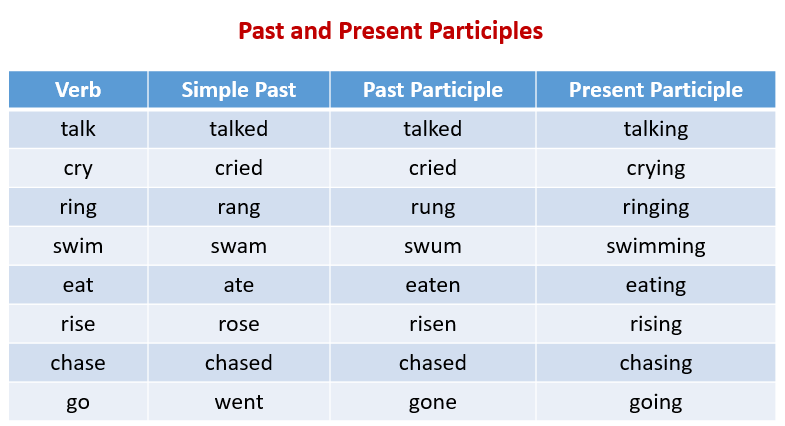
The following table gives some examples of present and past participles. Scroll down the page for more examples.
How to form the present participle?
We form the present participle by adding ing to the verb.
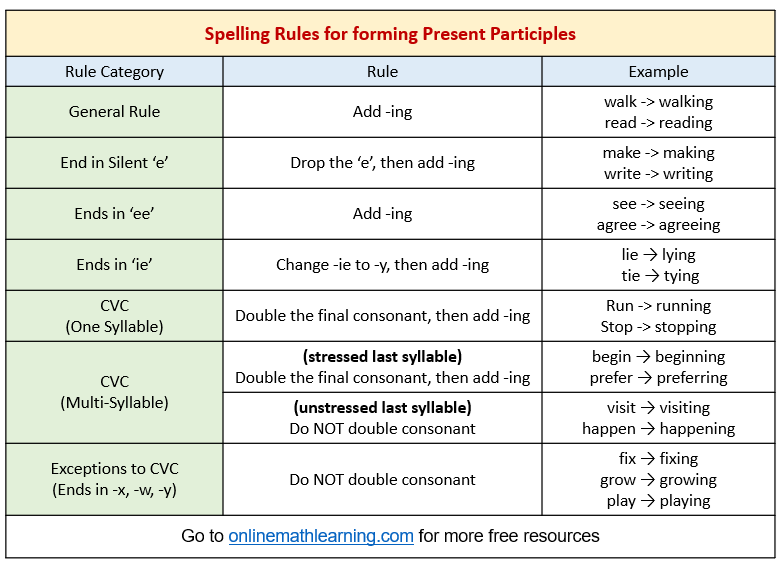
The following table gives some spelling rules for forming present participles. Scroll down the page for more examples.
When can we use the present participle?
-
We can use the present participle with the auxiliary verb to be to form the continuous tense.
Examples:
I am singing at the concert. (present continuous tense)
I was singing at the concert. (past continuous tense)
I will be singing at the concert. (future continuous tense) -
We can use the present participle to form the perfect continuous tense.
Examples:
I have been working. (present perfect continuous)
I had been working. (past perfect continuous)
I will have been working. (future perfect continuous) -
Present participles can also form adjectives.
Examples:
I can hear the bouncing ball.
These are his jogging shoes. -
As a Gerund (Noun):
When a verb ending in -ing functions as a noun, it’s called a gerund. It can be the subject of a sentence, a direct object, an object of a preposition, or a subject complement.
Swimming is good exercise. (Subject of the sentence)
I enjoy reading. (Direct object of “enjoy”)
She is good at painting. (Object of the preposition “at”)
My favorite activity is hiking. (Subject complement)
Spelling Rules for present participles
If the verb has one syllable, one vowel and ends with a consonant, double the last letter before adding ing.
Examples:
| Verb | Present Participle |
| get | getting |
| hit | hitting |
| jog | jogging |
| nod | nodding |
| rob | robbing |
| swim | swimming |
| stop | stopping |
| top | topping |
If a verb ends ends in silent ‘-e’, the silent ‘-e’ is dropped and ‘-ing’ is added.
Examples:
| Verb | Present Participle |
| chase | chasing |
| cycle | cycling |
| drive | driving |
| ride | riding |
| rise | rising |
| shake | shaking |
| shave | shaving |
| smile | smiling |
| take | taking |
| wave | waving |
If a verb ends with a single l, it is doubled in British English but not in American English.
| Verb | Present Participle |
British |
|
| dial | dialling |
| travel | travelling |
American |
|
| dial | dialing |
| travel | traveling |
What is a present participle adjective?
A present participle adjective is a word formed from a verb using the present participle or “ing” form of the verb.
This video shows some examples of present particles used as adjectives.
Participle adjectives ending in “ing” and “ed”
In this lesson you will learn:
- The origin of both participle adjectives ending in ING and ED and the form.
- The meaning and use of -ing and -ed adjectives.
- Some common examples of participle adjectives.
-ing adjectives are the present participle form of the verb.
-ed adjectives are the past participle form of the verb.
The adjectives that cause confusion for students are the ones that describe feelings and emotion. They cause confusion because both types can be used to describe people but the meaning is very different.
Common examples are:
interesting vs interested
boring vs bored
exciting vs excited
Compare the past tense, past participle and present participle
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.