Past Participle
Related Pages
Simple Past Tense
IELTS, TOEFL And English As A Second Language
More Lessons On English Grammar
In these lessons, we will learn:
- How past participles can be used in the present perfect tense?
- How past participles can be used in the past perfect tense?
- How past participles can be used in the future perfect tense?
- How past participles can be used to form modal verbs?
- Some commonly used irregular verbs: the base form (infinitive), past tense and past participle.
Verbs have different forms, called tenses. The tense of a verb tells us when the action happens. The past participle is a verb form that signals completed actions and can function as a powerful adjective to add detail and precision to your sentences.
The following table gives a summary of the forms and uses of past participles. Scroll down the page for more examples.
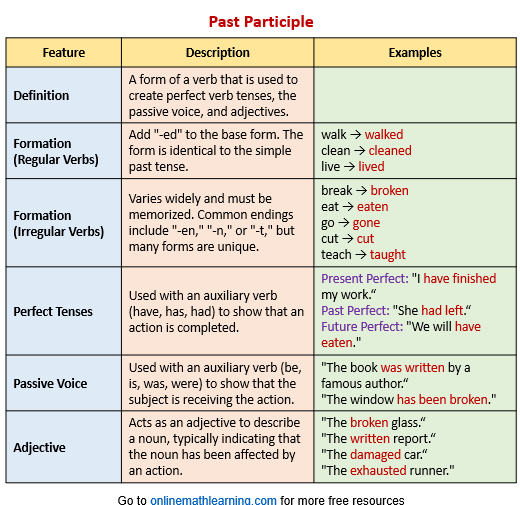
List of Past Participles of Regular Verbs
List of Past Participles of Irregular Verbs
How to Form the Past Participle
The way a past participle is formed depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular.
Regular Verbs: The past participle is the same as the simple past tense. You simply add “-ed” to the end of the base verb.
walk → walked
clean → cleaned
love → loved (just add “-d”)
Irregular Verbs: These verbs do not follow the “-ed” rule. Their past participle forms are unique and must be memorized. They can have various endings, such as “-en,” “-n,” “-t,” or can even stay the same.
break → broken
go → gone
sing → sung
cut → cut
The Three Main Uses of the Past Participle
The past participle is a versatile verb form with three primary functions:
1. To Form Perfect Verb Tenses
This is one of the most common uses. The past participle is used with an auxiliary verb (a form of “to have”: have, has, or had) to indicate a completed action.
Present Perfect: “I have finished my work.” (The action is completed but is relevant to the present.)
Past Perfect: “They had already eaten before we arrived.” (An action completed before another action in the past.)
Future Perfect: “By the time the sun sets, we will have driven for six hours.” (An action that will be completed by a specific time in the future.)
2. To Form the Passive Voice
In a passive voice construction, the past participle is used with a form of the auxiliary verb “to be” (am, is, are, was, were, been) to show that the subject is receiving the action, rather than performing it.
Active: “The dog chased the ball."
Passive: “The ball was chased by the dog."
Active: “The artist painted the masterpiece."
Passive: “The masterpiece was painted by the artist.”
3. As an Adjective
A past participle can be used as an adjective to describe a noun. In this role, it typically indicates that the noun has been affected by an action or is in a particular state.
“The broken vase was a family heirloom.” (The vase received the action of being broken.)
“He showed me his written report.” (The report received the action of being written.)
“The hikers were exhausted after the long climb.” (The hikers received the effect of exhaustion.)
The following table gives some examples of past and present participles. Scroll down the page for more examples.
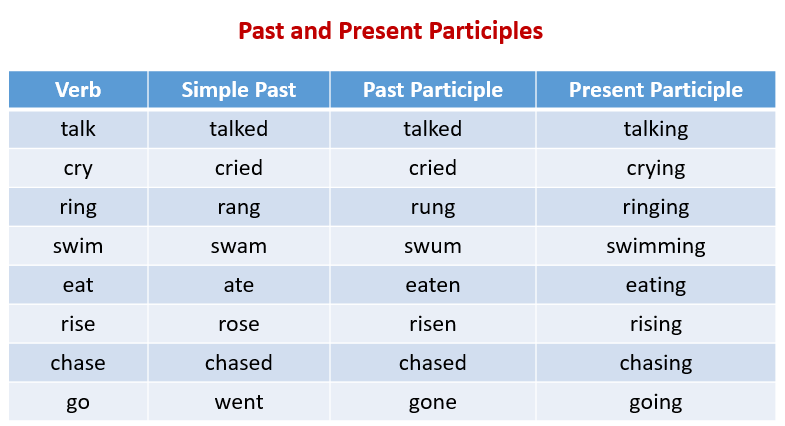
Past Participle
A past participle indicates a completed action.
For most verbs, the past participle is the same as the past tense and is created by adding a d, ed or ied at the end of the word. These are called regular verbs.
However, the past participles of irregular verbs do not end in ed and may not be the same as the past tense of the verb. Since they are irregular, they do not follow any pattern and the best way to learn them would be to repeat and memorize them.
Present Perfect Tense
We join have or has to the past participle of the verb to form the present perfect tense.
have/has + past participle = present perfect tense
Examples:
They have gone to the movies.
I have lost my wallet.
She has done her homework.
Have you found your keys yet?
It has not rained for months.
Martha has been sick.
Past Perfect Tense
We join had to the past participle to form the past perfect tense.
had + past participle = past perfect tense
Examples:
The bus had already left.
Suddenly he remembered where he had hidden the money.
Future Perfect Tense
We join shall have or will have to the past participle to form the future perfect tense.
shall have/will have + past participle = future perfect tense
Examples:
He will not have got up yet.
When you get this message, I shall have left for London.
When do you think that you will have finished that piece of work?
Modal Verbs
We join should have, could have or would have to the past participle to form modal verbs.
should have/could have/would have + past participle = modal verb
Examples:
They should have gone to the movies yesterday.
He could have been more attentive.
It would have been better if she had kept quiet.
This video will review common past participles. It will show you how they are used in American English, and help you better understand them when they are spoken in fast English. (Part 1)
This video will review common past participles and focus on how they sound in fast speech. (Part 2)
List Of Commonly Used Irregular Verbs
The following is a list of commonly used irregular verbs: the base form (infinitive), past tense and past participle.
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| arise | arose | arisen |
| awake | awoke | awoken |
| be | was, were | been |
| bear | bore | born/borne |
| beat | beat | beaten |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| behold | beheld | beheld |
| bend | bent | bent |
| bet | bet | bet |
| bid | bade | bidden |
| bid | bid | bid |
| bind | bound | bound |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| bleed | bled | bled |
| blow | blew | blown |
| break | broke | broken |
| breed | bred | bred |
| bring | brought | brought |
| build | built | built |
| burst | burst | burst |
| bust | bust | bust |
| buy | bought | bought |
| cast | cast | cast |
| catch | caught | caught |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| clap | clapped | clapped |
| cling | clung | clung |
| come | came | come |
| cost | cost | cost |
| creep | crept | crept |
| cut | cut | cut |
| dare | dared | dared |
| deal | dealt | dealt |
| dig | dug | dug |
| dive | dived | dived |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| dream | dreamt | dreamt |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| drive | drove | driven |
| dwell | dwelt | dwelt |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feed | fed | fed |
| feel | felt | felt |
| fight | fought | fought |
| find | found | found |
| flee | fled | fled |
| fling | flung | flung |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forbid | forbade | forbidden |
| foresee | foresaw | foreseen |
| foretell | foretold | foretold |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven |
| forsake | forsook | forsaken |
| freeze | froze | frozen |
| frostbite | frostbit | frostbitten |
| get | got | gotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| go | went | gone/been |
| grind | ground | ground |
| grow | grew | grown |
| handwrite | handwrote | handwritten |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hold | held | held |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| inlay | inlaid | inlaid |
| input | input | input |
| interlay | interlaid | interlaid |
| keep | kept | kept |
| kneel | knelt | knelt |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| learn | learnt | learnt |
| leave | left | left |
| lend | lent | lent |
| let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain |
| light | lit | lit |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| mean | meant | meant |
| meet | met | met |
| pay | paid | paid |
| quit | quit | quit |
| read | read | read |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| run | ran | run |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| seek | sought | sought |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| shake | shook | shaken |
| shine | shone | shone |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sit | sat | sat |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| spend | spent | spent |
| spring | sprang | sprung |
| stand | stood | stood |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| swim | swam | swum |
| swing | swung | swung |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| tear | tore | torn |
| tell | told | told |
| think | thought | thought |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| understand | understood | understood |
| wake | woke | woken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| win | won | won |
| write | wrote | written |
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.