Multiplication (Area Model)
Related Pages
Math Games
Multiplication Games
Multiplication Worksheets
This Multiplication (Area Model) also called the Box Method is a great way to put your multiplication skills to the test in a fun environment. This is a stepping stone to multi-digit multiplications.
Multiplication (Area Model)
This Multiplication (Area Model) is an interactive and engaging web-based application designed to help you practice your multiplication skills.
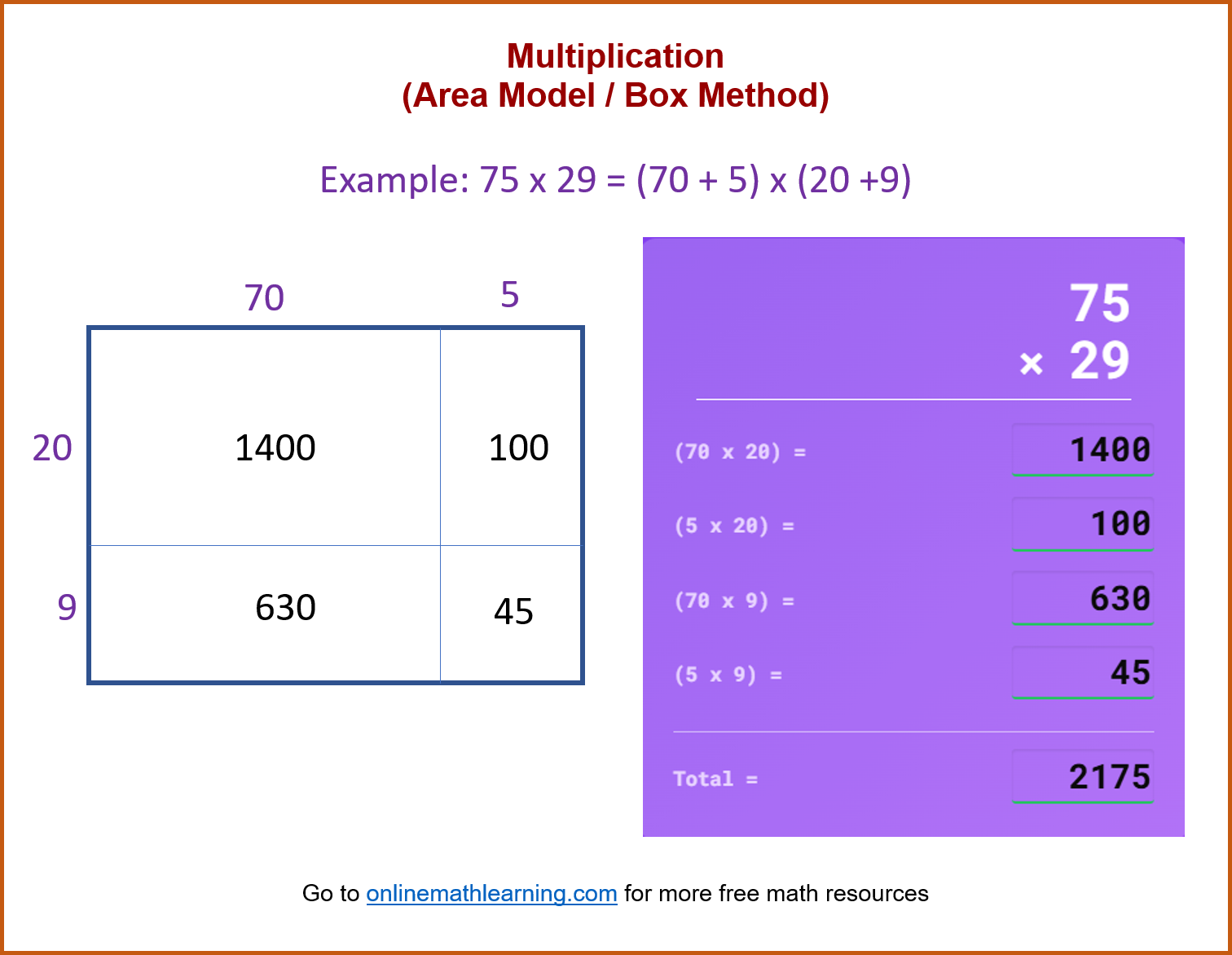
The Area Model or Box Method is a visual way to solve multiplication by breaking numbers apart into their expanded form (tens and ones). This method makes it much easier to keep track of place value and ensures you don’t miss any steps. This method helps visualize the multiplication process and is often used as a stepping stone to the standard multiplication algorithm. Scroll down the page if you need a more detailed explanation.
This Multiplication (Area Model) Game has an option to give a guide for the partial products.
Area Model
2-Digit x 2-Digit Multiplication
Area Model
Score: 0 / 0
How to Play the Multiplication Game (Area Model)
The game is designed to help you practice your Multiplication (Area Model) skills in a fun environment.
Here’s how to play:
- Step-by-step Guide: Check the “Show Step-by-Step Guide” if you want a guide for each step. (If you did not select the Guide then you can enter the steps in any order). Click “Start Game”.
- Look at the Problem: You’ll see two numbers at the top of the purple box. Your goal is to multiply them.
- Enter the Area Model: Type in the products for each. Add them up to get the total.
- Check Your Work: Click the yellow Check button (or press the Enter key). The game will tell you if you’re correct. If you are wrong, you will be shown which of the answers are wrong.
- Get a New Problem: Click the blue Next button (or press Enter again) for a new multiplication problem.
Your score is tracked at the top, showing how many you’ve gotten right out of the total you’ve tried. - Back to Menu Click “Back to Menu” to restart the game.
The Area Model for Multiplication
The Area Model is a visual way to solve multiplication by breaking numbers apart into their expanded form (tens and ones). This method makes it much easier to keep track of place value and ensures you don’t miss any steps.
The Concept: Breaking it Down
When we multiply 35 × 24, we are multiplying (30 + 5) × (20 + 4).
The Area Model gives us a box for every possible combination:
Tens × Tens
Tens × Ones
Ones × Tens
Ones × Ones
Here’s how it works:
Let’s use an example to illustrate the process: 35×24
Step-by-Step Example:
35 × 24
Step 1: Expand the Numbers
Write both numbers in expanded form:
35 = 30 + 5
24 = 20 + 4
Step 2: Draw the Grid
Create a 2 × 2 box. Place one number across the top and the other down the left side.
Step 3: Fill the Boxes (The 4 Multiplications)
Multiply the number at the top of the column by the number at the start of the row.
Top-Left: 20 × 30 = 600 (Think: 2 \times 3 = 6, then add two zeros)
Top-Right: 20 × 5 = 100
Bottom-Left: 4 × 30 = 120
Bottom-Right: 4 × 5 = 20
Step 4: Add the Partial Products
Now, add all four numbers inside the boxes together. You can add them in any order, but adding them by rows or columns is usually easiest:
Top Row: 600 + 100 = 700
Bottom Row: 120 + 20 = 140
Total: 700 + 140 = 840
Final Answer: 35 × 24 = 840
Why this works
The Area Model is great because it prevents the “Magic Zero” mistake found in the standard algorithm. By writing $20$ instead of just $2$, the place value is built right into the box.
Quick Tip: The “Zero Trick”
When multiplying numbers like 40 × 30:
Multiply the non-zero digits (4 × 3 = 12).
Count the total number of zeros in the problem (one from 40, one from 30 = two zeros).
Put that many zeros at the end (12 ⇒ 1200).
The video gives a clear, step-by-step approach to walk through the process of multiplying a 2-digit number by 2-digit number using Area Model or Box Method.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.