Derivatives of Exponential Functions
Related Pages
Exponential Functions
Derivative Rules
Natural Logarithm
Calculus Lessons
In these lessons, we will look at the derivatives of Exponential Functions.
Exponential Functions
The function f(x) = 2x is called an exponential function because the variable x is in the exponent or index. Do not confuse it with the function g(x) = x2, in which the variable is the base.
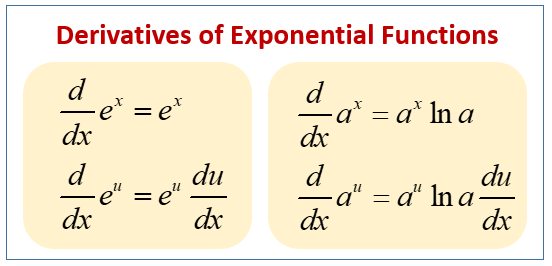
The following diagram shows the derivatives of exponential functions. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the derivatives of exponential functions.
Calculus Games/Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Calculus Games and Worksheets
In general, an exponential function is of the form
f(x) = ax where a is a positive constant.
There are two main types of exponential functions you’ll encounter, and their derivatives are closely related.
1. Derivative of the Natural Exponential Function: ex
Function: \(f(x) = e^x \)
Derivative: \(\frac{d}{dx}(e^x) = e^x\)
The exponential function f(x) = ex has the property that it is its own derivative. This means that the slope of a tangent line to the curve y = ex at any point is equal to the y-coordinate of the point.
We can combine the above formula with the chain rule to get
\(\frac{d}{dx}e^u = e^x \frac{du}{dx}\)
where u is a function of x
Example:
Differentiate the function y = e sin x
Solution:
\(\frac{d}{dx}(e^{\text{sin x}})= e^{\text{sin x}}\frac{d}{dx}(\text{sin x}) = e^{\text{sin x}}\text{cos x} \)
Example:
Differentiate the function y = e–3xsin4x
Solution:
Using the Product Rule and the above formulas, we get
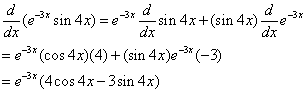
2. Derivative of a General Exponential Function: ax
For any positive constant base a (where a > 0 and a ≠ 1)
Function: \(f(x) = a^n \)
Derivative: \(\frac{d}{dx}(a^x) = a^x \text{ln } a\)
Using the chain rule, we get
\(\frac{d}{dx}a^u = a^u \text{ln }a \frac{du}{dx}\)
where u is a function of x
Example:
\(\frac{d}{dx} a^{g(x)} = a^{g(x)} \text{ln }a g’(x)\)
Example:
Differentiate y = x3 + 3x
Solution:
\(\frac{d}{dx}(x^3 + 3^x) = 3x^2 + 3^x(\text{ln }3) \)
Example:
Differentiate y = 52x+1
Solution:
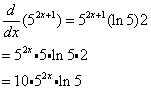
Derivatives of Exponential Functions
The derivative of an exponential function can be derived using the definition of the derivative.
Derivatives of exponential functions involve the natural logarithm function, which itself is an
important limit in Calculus, as well as the initial exponential function. The derivative is the
natural logarithm of the base times the original function.
Derivatives of Exponential Functions with Base e
Exponential Functions and Derivatives
This video gives the formula to find derivatives of exponential functions and does a few
examples of finding derivatives of exponential functions.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.