How to Simplify Equations (Combine Like Terms)
Related Pages
Isolate A Variable
Algebraic Expressions
More Algebra Lessons
Simplifying equations is often the first step to solving algebra equations. Some methods that can be used to simplify an equation are Combine Like Terms, Multiplication & Division of Terms, Removal of Brackets (Distributive Property) and Cross Multiplication.
Combining Like Terms
Simplifying equations by combining like terms is a fundamental step in solving algebraic equations. It involves identifying terms that have the same variable raised to the same power and then adding or subtracting their coefficients. This process makes the equation easier to work with and eventually solve for the unknown variable. Combining like terms is very often required in the process of simplifying equations.
The following diagrams show how to combine like terms to simplify an expression. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
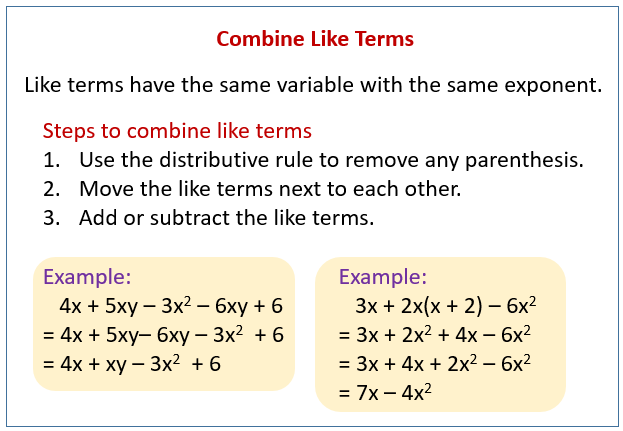
Algebra Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Algebra worksheets:
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
Identify Like Terms
Like terms are terms that have the
same variable(s) with the same exponent(s). They only differ in their
coefficients.
For example:
\(2x\) and \(-5x\) are like terms.
\(a\) and \( \frac{1}{2} a \) are like terms.
\(6\) and \(5y\) are unlike terms.
Like terms can be added or subtracted from one another.
Example:
\(a + a = 2 \times a = 2a\) (We usually write \(2 \times a \) as \(2a\))
\(2a + 4a = 6a\)
\(a + a + a = 3a\)
\(6a - 3a = 3a\)
\(8b - 8b = 0\)
Unlike terms cannot be simplified.
Example:
\(2a + 4\)
\(4a + 3b\)
\(5a - 3\)
\(6a - 4b\)
Example 1:
Simplify:
\(8xy - 5yx = 1\)
Solution:
Step 1: \(5yx\) is the same as \(5xy\) using the commutative property
Step 2: Since the right side is already simple, we can work on the left side expression
\(8xy - 5yx = 8xy - 5xy = 3xy\)
Putting back the left side and right side of the equation:
\(3xy = 1\)
Answer: \(3xy = 1\)
Example 2:
Simplify: \(7a + 5b - 6b + 8a + 2b = 0\)
Solution:
Step 1: Group together the like terms:
\(7a + 5b - 6b + 8a + 2b = 0\)
\((7a + 8a) + (5b - 6b + 2b) = 0\)
Step 2: Then simplify:
\(15a + b = 0\)
Answer: \(15a + b = 0\)
How To Solve An Equation By Combining Like Terms?
Multiplication And Division Of Terms
The coefficients and variables of terms can be multiplied or divided together in the process of simplifying equations.
For example:
3 × 4b = 3 × 4 × b = 12b
5a × 3a = 5 × a × 3 × a = 5 × 3 × a × a = 15a2 (using exponents)
Be careful!
a × a = a2
a + a = 2a
Example:
Simplify: 4a × 5a ÷ 2a = 60
Solution:
Step 1: Perform the multiplication and division

Step 2: Isolate a
![]()
Answer: a = 6
How To Solve Equations Using Multiplication Or Division?
Removal Of Brackets - Distributive Property
Sometimes removing brackets (parenthesis) allows us to simplify the expression. Brackets can be removed by using the distributive property. This is often useful in simplifying equations.
For example:
3(a – 3) + 4 = 3 × a + 3 × (-3) + 4 = 3a – 9 + 4 = 3a – 5
5 – 6 (b + 1) = 5 + ( – 6 ) × b + (– 6) × 1 = 5 – 6b – 6 = – 6b – 1
Example 1:
Simplify: 5(a – 4) + 3 = 8
Solution:
Step 1: Remove the brackets
5a – 20 + 3 = 8
Step 2: Isolate variable a
5a = 8 – 3 + 20
5a = 25
![]()
Answer: a = 5
How To Solve An Equation By The Distributive Property?
Cross Multiplication
Cross multiplication allows you to remove denominators from fractions in an equation. Note that this technique applies only towards simplifying equations, not to simplifying expressions.
For example, if you have the equation:
![]()
then you can multiply the numerator of one fraction with the denominator of the other fraction (across
the = sign) as shown:

to obtain the equation
(2 × 6) = a × 3
Example 1:
Simplify: ![]()
Solution:
Step 1:Cross Multiply
4 × a = 8 × 5
4a = 40
Step 2: Isolate variable a
![]()
Answer: a = 10
How To Solve Equations Easily By Cross-Multiplying When There Are Two Fractions
How To Solve Fraction Equations By Isolating The Variable Using Inverse Operations?
Have a look at the following video for more examples on simplifying equations.
How To Simplify And Solve Equations?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.