Transformed Trig Graph Game
Related Pages
Printable Math Worksheets
Online Math Quizzes
Math Games
Math Worksheets
We can visualize trigonometry by looking at the transformed graphs for the Sine and Cosine waves. This game is a step-up in difficulty from the Basic Trig Graph Game for Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant.
Transformed Trig Graph Quiz/Game
This game, “Transformed Trig Graphs,” is a training tool designed to help you master the functional transformations of Sine and Cosine waves. Instead of just identifying the basic function, you have to decode how the wave that has been stretched, moved, and shifted. Scroll down the page for a more detailed explanation.
Analyze the Wave:
How to Play
- Analyze the Wave:
Look at where the yellow line starts, where it crosses the center axis (the x-axis), and if it has any “gaps” (asymptotes). - Pick Your Answer:
You are given four equations in the form y = A · f(x - C) + D. - Select the Match:
Click one of the four buttons.
Green Flash: You matched correctly
Red Flash: You missed it. The game will immediately highlight the correct answer in green so you can memorize it for the next round. - Next Question: Click the Next Question button to generate a brand-new random graph.
- Scoring and Content
The game tracks your progress in the top-left corner (Score: Correct / Total Attempts).
Transformation of Trig Graphs
Transforming trigonometric graphs is like using a set of remote controls to stretch, squish, and move a wave. The standard “parent” functions, y = sin(x) and y = cos(x), are manipulated using the general formula:
y = A · f(B(x - C)) + D
Each letter represents a specific physical change to the wave.
Amplitude (A): The Height
The coefficient A controls the vertical stretch or compression. It measures the distance from the center “midline” to the peak (or trough).
If |A| > 1: The graph stretches vertically (becomes taller).
If 0 < |A| < 1: The graph shrinks vertically (becomes flatter).
Negative A: If A is negative, the entire graph is reflected over the horizontal axis (it flips upside down).
Period (B): The Width
The value B affects the horizontal stretch or compression. It tells you how many cycles happen within the standard 2π space.
Formula for Period: \(P = \frac{2\pi}{B}\)
If B > 1: The graph is horizontally compressed (the wave repeats more frequently).
If 0 < B < 1: The graph is horizontally stretched (the wave slows down).
Phase Shift (C): Horizontal Movement
The value C moves the graph left or right. This is often the trickiest part because the sign in the parentheses is “counter-intuitive."
(x - C): The graph shifts to the right.
(x + C): The graph shifts to the left.
Note: If there is a B value, you must factor it out (e.g., sin(2x - π) becomes sin(2(x - π/2))) to find the true phase shift.
Vertical Shift (D): The Midline
The constant D at the end of the equation moves the entire graph up or down.
It defines the new midline (the equilibrium point the wave oscillates around).
- D: Moves the graph up.
- D: Moves the graph down.
Example Strategy
Imagine the graph shows a wave that:
Is centered at y = 1 (Vertical Shift is +1).
Goes up to y=3 and down to y=-1 (Distance from center is 2, so Amplitude is 2).
Starts at its peak on the y-axis (It’s a cos function).
You would look for the button that says:
y = 2cos(x) + 1
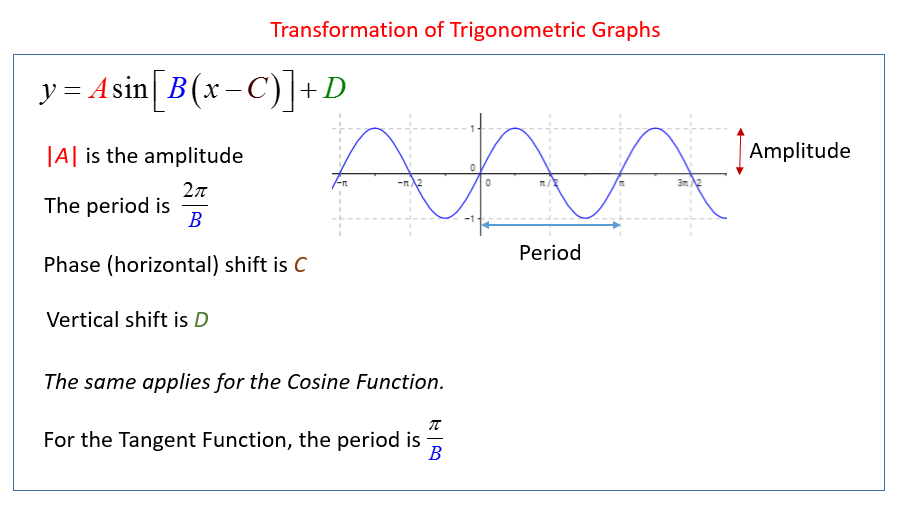
Have a look at this lesson on Transformation of Trig Function Graphs
Graphing Trig Functions
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.