Position Vector
Related Pages
Vectors
Equal Vectors
Vector Multiplication
Vector Geometry
In these lessons, we will learn what a position vector is and how to find a position vector for a vector between two points.
What Is A Position Vector?
A position vector describes the location of a point in space relative to a fixed reference point (usually the origin O of a coordinate system). The other end of the position vector terminates at the specific point whose position you are trying to describe. The direction of the position vector always points from the origin towards the given point.
In the following diagram, point A has the position vector a and point B has the position vector b.
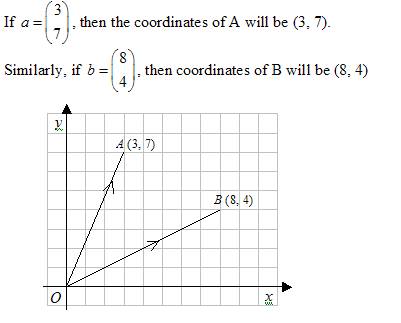
Example:
Tutorial On Vectors
What are 2-dimensional Vectors, 3-dimensional Vectors, Displacement Vectors and Position Vectors?
How To Find The Position Vector?
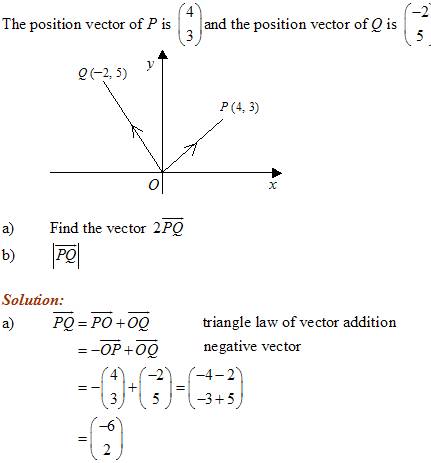
Example:
P is the point (3, 4). \(\overrightarrow {PQ} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - 6}\\3\end{array}} \right)\).
Find the position vector of Q.
Vectors In R2 And R3
Position Vector and Magnitude / Length.
How to find a position vector for a vector between two points and also find the length of the vector?
Example:
a) Find the position vector v for a vector that starts at Q(3, 7) and ends at P(-4, 2)
b) Find the length of the vector found in part a)
How To Find The Position Vector Between Two Points?
Example:
Find the position vector between the point A(3, 2) and the point B(-2, 1)
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.