Chemistry Required Practical: Identifying Ions
Related Topics:
GCSE/IGCSE Chemistry
Chemistry Required Practicals
GCSE/IGCSE Physics
GCSE/IGCSE Biology
GCSE/IGCSE Maths
GCSE Chemistry Required Practical - Identify Ions
Use of chemical tests to identify the ions in unknown single ionic compounds.
In this practical you will:
- use flame tests and add a range of solutions to analyse a range of known ionic compounds
- use your results to identify the ions present in an unknown solution
Describe flame tests to identify the following ions in solids:
- lithium ion, Li+ burns with crimson flame
- sodium ion, Na+ burns with yellow flame
- potassium ion, K+ burns with lilac flame
- calcium ion, Ca2+ burns with orange-red flame
- copper ion, Cu2+ burns green flame
The following diagram shows how to identify some anions in a solution. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
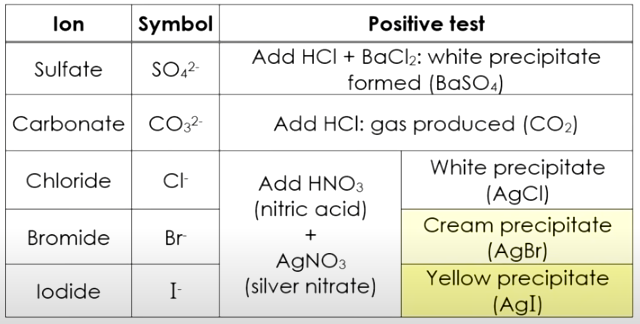
Method
Activity 1: Flame Tests
- Pour about 1 cm depth of each of the labelled chloride solutions into five test tubes in the rack.
- Dip the nichrome wire into the first solution. Then hold the tip of the wire in a blue Bunsen burner flame.
- Record your observation a table
- Clean the wire carefully.
- Repeat steps 2‒4 for each of the other four solutions.
- Empty and clean the test tubes.
Activity 2: Carbonate test
- Pour about 1 cm depth of each of the labelled sodium solutions into five test tubes in the rack.
- Place 1 cm depth of limewater in a sixth test tube.
- Add 1 cm depth of dilute hydrochloric acid to each sodium salt solution in turn.
- Only if you see bubbles, quickly use the teat pipette to transfer the gas produced to the limewater. You should pipette the gas into the limewater solution. Your teacher may show you how to do this.
- You will need to take several pipettes of the gas coming off at the surface to get a change in the limewater.
- Record your results in a table.
- Empty and clean the test tubes.
Activity 3: Sulfate test
- Pour about 1 cm depth of each of the labelled sodium solutions into five test tubes in the rack.
- Add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid to each solution. Then add 1 cm depth of barium chloride solution.
- Record your observations in the table.
- Empty and clean the test tubes.
Activity 4: Halide test
- Pour about 1 cm depth of each of the labelled sodium solutions into five test tubes in the rack.
- Add a few drops of dilute nitric acid to each solution. Then add 1 cm depth of silver nitrate solution.
- Record your observations in the table.
Identifying Ions
How to test for metal and non-metal ions using flame, bubble and precipitation tests?
00:00 Flame tests for metal ions
05:01 Precipitate tests for non-metal ions
05:45 Test for carbonate ions
06:52 Test for sulfate ions
07:40 Test for halogen ions
GCSE Science Chemistry Required Practical: Identifying Ions
Describe how to use chemical tests to identify the ions in unknown compounds.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.