Solving Equations With Variables On Both Sides
Related Pages
Solving Equations
Basic Algebra
Combining Like Terms
Algebra - Transposition
More Algebra Lessons
In these lessons, we will learn to solve equations that have a term with the variable on both sides of the equation.
Solving multi-step equations with variables
Solving multi-step equations with variables on both sides builds upon the skills you’ve learned for solving simpler equations. The key is to strategically move the variable terms to one side of the equation and the constant terms to the other side before isolating the variable.
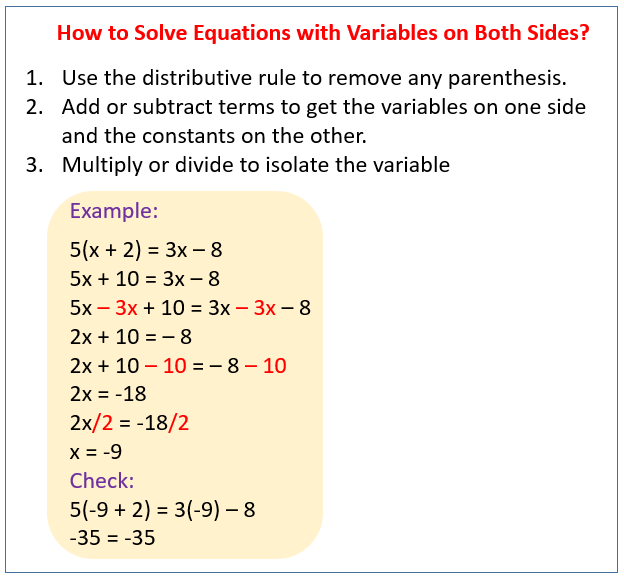
The following figure shows how to solve equations with variables on both sides. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
Algebra Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Algebra worksheets:
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
-
Simplify Each Side of the Equation:
a. Distribute: If there are any parentheses, use the distributive property to multiply the term outside the parentheses by each term inside.
Example: 2(x + 3) = 2x + 6
b. Combine Like Terms: If there are like terms on the same side of the equation, combine them by adding or subtracting their coefficients.
Example: 3y - 5 + 2y = 5y - 5 -
Move Variable Terms to One Side:
a. Use addition or subtraction to get all the terms containing the variable onto one side of the equation.
b. It’s often easier to move the variable term with the smaller coefficient to the side with the larger coefficient to avoid dealing with negative coefficients if possible.
c. Remember to perform the same operation on both sides of the equation to maintain balance. -
Move Constant Terms to the Other Side:
a. Use addition or subtraction to get all the constant terms (numbers without variables) onto the side opposite the variable terms.
b. Again, perform the same operation on both sides to maintain balance. -
Isolate the Variable:
a. Once you have a single variable term on one side and a constant term on the other, use multiplication or division to isolate the variable.
b. If the variable is being multiplied by a coefficient, divide both sides by that coefficient.
c. If the variable is being divided by a number, multiply both sides by that number. -
Check Your Solution:
a. Substitute the value you found for the variable back into the original equation.
b. Simplify both sides of the equation.
c. If both sides are equal, your solution is correct.
Example:
Consider the equation x – 6 = –2x + 3.
To isolate the variable, we need to get all the variable terms to one side and the constant terms
to the other side. Next, we combine like terms and then isolate the variable by multiplying or dividing.
Solve x – 6 = –2x + 3
Solution:
Step 1: Get all the variable terms to one side and the constant
terms to the other side.
x – 6 = –2x + 3
x – 6 + 2x + 6 = –2x + 3 + 2x + 6 (Add 2x & 6 to
both sides)
Step 2: Combine like terms
2x + x = 3 + 6
3x = 9
Step 3: Divide or multiply to isolate the variable
3x = 9 (Divide by 3)
x = 3
Check:
x – 6 = –2x + 3
3 – 6 = –2 • 3 + 3 (substitute x = 3 into
the original equation)
–3 = –3
Example:
Consider the equation 6x – 4 = 3x + 2. To isolate the variable, we need to get all the
variable terms to one side and the constant terms to the other side. Next, we combine like
terms and then isolate the variable by multiplying or dividing.
Solve 6x – 4 = 3x + 2
Solution:
Step 1: Get all the variable terms to one side and the constant
terms to the other side.
6x – 4 = 3x + 2
6x – 4 – 3x + 4 = 3x + 2 – 3x + 4 (Subtract 3x &
add 4 to both sides)
Step 2: Combine like terms
6x – 3x = 2 + 4
3x = 6
Step 3: Divide or multiply to isolate the variable
3x = 6 (Divide by 3)
x = 2
Check:
6x – 4 = 3x + 2 (substitute x = 2 into the original equation)
6 • 2 – 4 = 3 • 2 + 2
8 = 8
How to solve equations with variables on both sides of the equation?
Examples:
- 5x + 8 = 7x
- 4w + 8 = 6w – 4
- 6(g + 3) = – 2(g + 31)
Solving Equations with Variables on Both Sides
Step 1: Add and subtract terms to get the variables on one side and the constants on the other.
Step 2: Multiply or divide to isolate the variable.
Examples:
- 2x + 7 = 4x – 7
- 3x + 19 = 3 – 5x
Equations With Variables on Both Sides
This requested video looks at solving equations with variables on both sides. It includes four examples.
Examples:
- x + 14.8 = 102 – 7x
- 5y – 2 = 28 – y
- 3 + 5m = 8m – 9
- 4 + 3x – 6 = 3x + 2 – x
How to use the distributive property to simplify equations with variables on both sides?
Examples:
- 3(x – 1) = 2(x + 3)
- z/6 = 2(z + 1)/9
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.