Algebra Lesson - Transposition
Related Pages
Basic Algebra
Combining Like Terms
Solving Equations
More Algebra Lessons
In these lessons, we will learn one of the basic techniques of simplifying an algebraic equation so that we can eventually solve the equation.
This may be your first algebra lesson. In case you are rather uncomfortable with algebra, you may want to first go through Basic Algebra - An Introduction, which would give you a good foundation before this lesson.
Algebra Lesson - Transposition: Some Examples
Algebraic transposition, also known as “rearranging formulas” or “changing the subject of a formula,” is a fundamental skill in algebra. It’s the process of manipulating an equation to isolate a specific variable on one side, while moving all other terms to the other side.
The core principle behind transposition is maintaining the balance of the equation. Whatever operation you perform on one side of the equals sign, you must perform the exact same operation on the other side. This ensures that the equation remains true and equivalent to the original.
Transposition relies on using inverse operations to “undo” what’s being done to the variable you want to isolate.
The following are some examples of Algebra Transposition. Scroll down the page for more examples and step by step solutions.
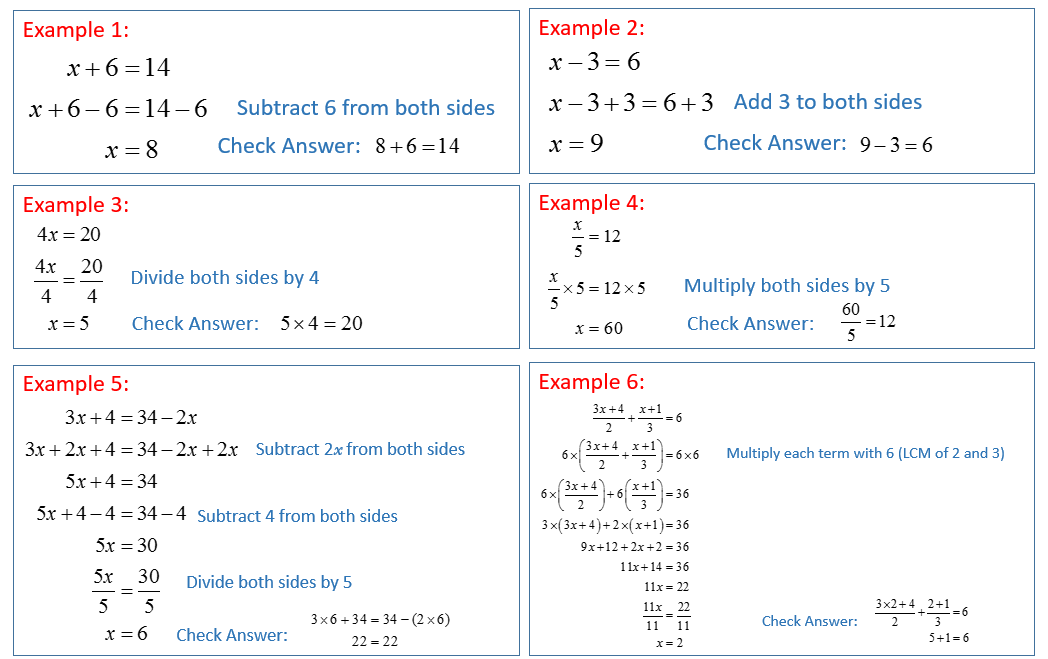
We have lots of Printable and Online Algebra Worksheets to help you to review and practice your Algebra skills.
This Algebra Lesson introduces a technique known as ’transposition’. This is the most common way to solve algebra equations. A quick review here of the basic principles - all equations have two sides: a Left Side (LS) and a Right Side (RS). In the example below 3x + 4 is on the Left Side of the equation and 31 is on the Right Side of the equation:
3x + 4 = 31
LS RS
The common transposition method is to do the same thing (mathematically) to both sides of the equation, with the aim of bringing like terms together and isolating the variable (or the unknown quantity).
So, to solve this equation, first subtract 4 from both sides of the equation. This will get rid of number 4 from the LS
3x + 4 - 4 = 31 - 4
That will give us:
3x = 27
Now, looking at the LS we have 3x. So we need to divide it by 3 to isolate x, and we need to do the same to the RS.
\(\frac{{3x}}{3} = \frac{{27}}{3}\)
Now that gives us:
\(x = \frac{{27}}{3} = 9\)
Check Our Answer:
Now, we have x = 9. We can substitute this value in the original equation to check if our answer is correct:
3x + 4 = 31
3 × 9 + 4 = 31
27 + 4 = 31
31 = 31
So, our answer x = 9 is correct.
That’s the algebra lesson on transposition. Now, you are ready to review some examples to further develop your understanding of transposition.
Transposition (Rearranging Equations) - Introduction
What is transposition? What is it used for?
Transposition (Rearranging Equations) - 1
How to transpose (or rearrange) equations?
How to solve equations?
- Remove fractions
- Remove brackets
- Move added/subtracted terms
- Divide by the number next to the letter
Transposition (Rearranging Equations) - 2
Include added and subtracted terms
Transposition (Rearranging Equations) - 3
Add brackets to the set of equations that we’ve already learned how to transpose
Transposition (Rearranging Equations) - 4
Include all the steps
Algebra Lesson - Transposition: Practice Questions
Algebra Worksheets and Practice Questions
Having completed the practice questions, you are now ready for other algebra lessons, like Substitution.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.