Using Similar Triangles
Related Topics:
Common Core (Geometry)
Common Core for Mathematics
Common Core: HSG-SRT.B.5
Examples, solutions, videos, and lessons to help High School students learn how to use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures.
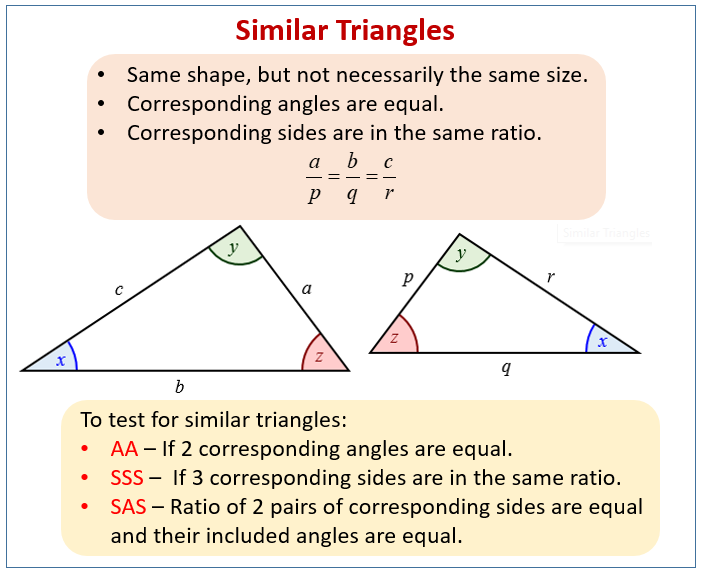
Similar Triangles
Similar triangles are triangles that have the exact same shape but can be different in size. One similar triangle is essentially a scaled version (an enlargement or a reduction) of the other.
The symbol for similarity is ~. So, if triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF, we write △ABC∼△DEF. When writing the similarity statement, it’s crucial to list the vertices in corresponding order.
The following diagrams show the properties of similar triangles. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to identify similar triangles and how to use similar triangles to solve problems.
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
Key Properties of Similar Triangles:
If two triangles are similar (△ABC∼△DEF):
-
Corresponding Angles are Equal (Congruent):
∠A = ∠D
∠B = ∠E
∠C = ∠F -
Corresponding Side Lengths are Proportional:
The ratio of the lengths of any pair of corresponding sides is constant. This constant ratio is called the scale factor.
\(\frac{AB}{DE} = \frac{BC}{EF} = \frac{AC}{DF} = k\) (where k is the scale factor) -
Ratio of Perimeters:
The ratio of the perimeters of two similar triangles is equal to their linear scale factor. -
Ratio of Areas:
The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of their linear scale factor. -
Ratio of Other Corresponding Linear Measurements:
The ratio of corresponding altitudes, medians, angle bisectors, or radii of inscribed/circumscribed circles is also equal to the linear scale factor k.
Find Missing Measures Using Similar Triangles
Similar triangles have equal corresponding angles and proportional sides. We can use these properties to find missing side lengths or heights in real-world problems (like shadow measurements, map scaling, or indirect height calculations).
-
Identify Similar Triangles
Look for two triangles where:
All corresponding angles are equal (AA Similarity), or
Two sides are proportional and the included angles are equal (SAS), or
All three sides are proportional (SSS). -
Set Up a Proportion
Since corresponding sides are proportional:
\(\frac{\text{Side in Triangle A}}{\text{Corresponding Side in Triangle B}}=\frac{\text{Unknown Side in Triangle A}}{\text{Corresponding Side in Triangle B}}\) -
Solve the Proportion:
Use cross-multiplication or other algebraic methods to solve for the unknown variable.
Finding missing measures using similar triangles
Use similar triangles to find unknown measures (angles and sides).
Indirect Measurement Using Similar Triangles
This video explains how to use the properties of similar triangles to determine the height of a tree.
Use Similar Triangles to Solve Problems
This lesson works though three examples of solving problems using similar triangles.
Example 1: Fred needs to know how wide a river is. He takes measurements as shown in the diagram. Determine the river’s width
Example 2: Determine the ratio of the areas of the two similar triangles.
Example 3: If the area of the smaller triangle is 20 m2, determine the area of the bigger triangle.
Application of Similar Triangles
Example:
An abstract artist wants to create two proportional triangular paintings. The dimensions are as shown. How long should the two missing sides be in the second painting?
How Tall Is It (The height of the light pole)
A lesson on using similar triangles and proportions to solve for a missing length.
Using Similar Triangles
Examples of applications with similar triangles.
- A tree with a height of 4 m casts a shadow 15 m long on the ground. How high is another tree that casts a shadow which is 20 m long?
- Jordan wants to measure the width of a river that he can’t cross. Help him to figure out the width of the river.
Indirect Measurement using Similar Triangles
Example:
Benjamin places a mirror 40 ft from the base of an oak tree. When he stands at a distance of 5 ft from the mirror, he can see the top of the tree in the reflection. If Benjamin is 5 ft 8 in tall, what is the height of the oak tree?
Word Problems with Similar Triangles and Proportions
Examples:
- Two ladders are leaning against a wall at the same angle. How long is the shorter angle?
- Campsites R and S are on opposite sides of a lake. What is the distance between the two campsites?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.