Set Theory: Universal Set
Related Pages
More Lessons On Sets
Subsets
Venn Diagrams
In these lessons, we will learn what is a universal set and how it may be represented in a Venn Diagram.
What Is The Universal Set?
The universal set is the set of all elements under consideration, denoted by capital U or sometimes capital E or ξ.
The following diagram explains what is a Universal Set and gives an example of a Universal Set. Scroll down the page if you need more explanations and examples about Universal Sets.
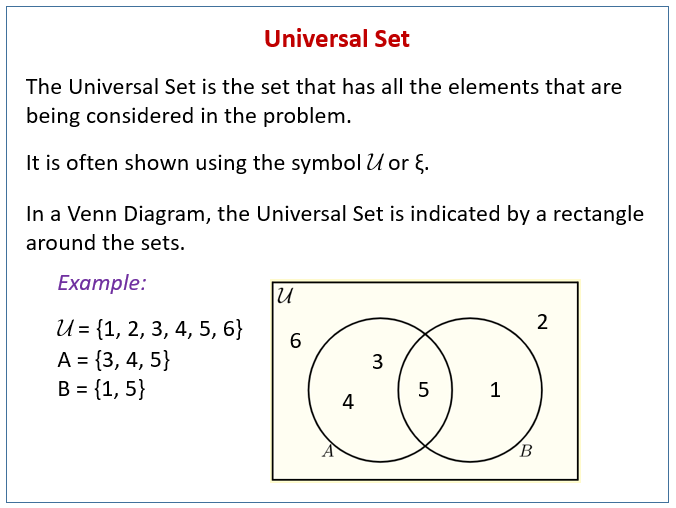
Properties of Universal Sets
- All-Inclusive:
Every other set in the discussion is a subset of U.
Example: If U = {1,2,3,4,5}, then A = {2,4} is a subset of U. - Complement of a Set:
The complement of set A (written A′ or Ac) includes all elements not in A but still in U.
A′ = U − A
Example: If U = {1,2,3,4} and A = {1,2}, then A′ = {3,4}. - Union/Intersection:
The union of any set with U is U: A ∪ U = U.
The intersection of any set with U is the set itself: A ∩ U = A.
Relationship with Venn Diagrams: In Venn diagrams, the universal set is typically represented by a rectangle, and all the subsets under consideration are drawn as circles within this rectangle.
Example:
Given that U = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}, list the elements of the following sets.
a) A = {x : x is a factor of 60}
b) B = {x : x is a prime number}
Solution:
The elements of sets A and B can only be selected from the given universal set U.
a) A = {5, 6, 10, 12}
b) B = {5, 7, 11}
In Venn diagrams, the universal set is usually represented by a rectangle and labeled U.
Example:
Draw a Venn diagram to represent the following sets:
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, A = {1, 2, 5, 6}, B = {3, 9}
Solution:
Step 1: Draw a rectangle and label it U to represent the
universal set.
Step 2: Draw circles within the rectangle to represent the other sets. Label the circles and write the relevant elements in each circle.
Step 3: Write the remaining elements outside the circles but within the rectangle.

The Universal Set And Set Complements
Example:
Let the universal set, U = {a, e, i, o, u}
Let the subset A = {a, e}
Then the complement of set A, A’ = {i, o, u}
Intersection, Union And Complement Of Sets
A ∩ B (read as A intersection B) are members that are common to both set A and set B.
A ∪ B (read as A union B) are members that are in set A or set B or both.
A’ (read as A complement) are members that are not in set A.
What Is Universal Set And Absolute Complement?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.