

Unit Vector and Components of a Vector
Vectors
Unit Vectors in Physics
Next set of math lessons in this series
Unit Vector
A unit vector is a vector with a magnitude of one unit.
Any vector has an associated unit vector in the same direction but having a magnitude of one. Any vector can be
expressed as a scalar multiple
of its unit vector.
The following diagram shows how to normalize a vector or how to determine a unit vector. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions of how to find a unit vector.
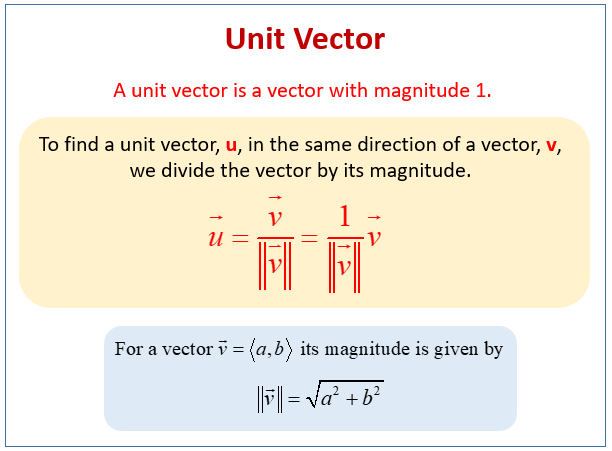
Finding the Unit Vector given a vector (divide the vector by its magnitude).
How to express a vector algebraically in terms of the unit vectors i and j. This video explains how to determine a unit vector given a vector. It also explains how to determine the component form of a vector in standard position that intersects the unit circle. Expressing a vector as the scaled sum of unit vectors. Unit Vector Notation (part 2).
Showing that adding the i and j components of two vectors is equivalent to adding the vectors visually using the head-to-tail method. Next set of videos in this series
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.