Median From Frequency Tables
Related Pages
Median
Mean And Mode From The Frequency Table
Central Tendency
More Statistics Lessons
In these lessons, we will learn:
- how to find the median of a frequency table when the number of observations is odd.
- how to find the median of a frequency table when the number of observations is even.
- how to find the median for both discrete and grouped data.
What Is The Median?
The median is the middle value in an ordered set of data.
In a frequency table, the observations are already arranged in an ascending order. We can obtain the median by looking for the value in the middle position.
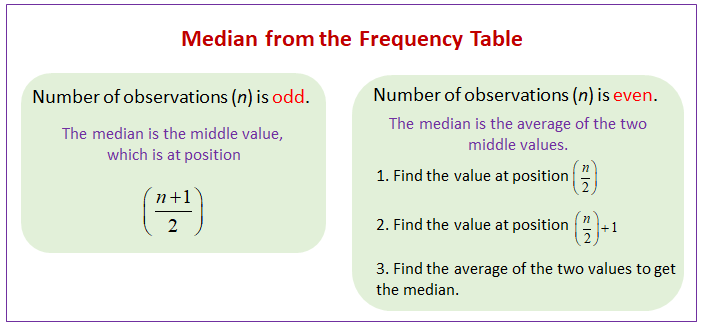
If there is an odd number of observations, the median is the middle number.
If there is an even number of observations, the median will be the mean of the two central numbers.
The following table shows how to find the median from the frequency table with odd number of observations and with even number of observations. Scroll down the page for examples and step-by-step solutions.
Statistics Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Statistics Worksheets
How To Find The Median Of A Frequency Table When The Number Of Observations Is Odd?
Case 1. When the number of observations (n) is odd, then the median is the value at the \(\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)^{th}\) position.
Steps:
- Sum all the frequencies to get the total frequency (n).
- Calculate Cumulative Frequencies:
Add a new column for cumulative frequency. This shows the running total of frequencies as you go down the table.
The first cumulative frequency is the same as the first frequency.
Each subsequent cumulative frequency is the sum of the current frequency and the previous cumulative frequency. - The position of the median is given by the formula: Position = \(\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)\)
- Locate the Median Value:
Find the first cumulative frequency that is greater than or equal to the median position you calculated in step 3.
The data value corresponding to this cumulative frequency is your median.
Example:
The following is a frequency table of the score obtained in a mathematics quiz. Find the median score.
| Score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 3 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 3 |
Solution:
Sum all the frequencies to get the number of scores.
Number of scores = 3 + 4 + 7 + 6 + 3 = 23 (odd number)
Since the number of scores is odd, the median is at the \(\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)^{th} = \left( \frac{23+1}{2} \right)^{th} = 12^{th}\) position.
To find out the 12 th position, we need to add up the frequencies, to find the cumulative frequencies, as shown:
| Score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 3 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 3 |
| Cumulative Frequency | 0 + 3 = 3 | 3 + 4 = 7 | 7 + 7 = 14 | 14 + 6 = 20 | 20 + 3 = 23 |
We need to find the data value for the 12th position. The first cumulative frequency that is greater than or equal to the 12th median position is 14. The data value (score) corresponding to this cumulative frequency is 2.
So the median is 2.
How To Find The Median Of A Frequency Table When The Number Of Observations Is Even?
Case 2. When the number of observations (n) is even, then the median is the average of values at the \(\frac{n}{2}\) and \(\frac{n}{2} + 1\) positions.
Steps:
- Sum all the frequencies to get the total frequency (n).
- Calculate the cumulative frequencies.
- The position of the median is given by the formula: Position = \(\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)\)
- Locate the Median Value:
Determine the Positions of the Two Middle Values:
The first middle position is \(\frac{n}{2}\).
The second middle position is \(\frac{n}{2} + 1\). - Locate the Values:
Use the cumulative frequency column to find the data value (x1) corresponding to the \(\left(\frac{n}{2}\right)^{th}\) position.
Use the cumulative frequency column to find the data value (x2) corresponding to the \(\left(\frac{n}{2} + 1\right)^{th}\) position. - The median is the average of these two data values: \(\frac{x_1 + x_2}{2}\)
Example:
The table is a frequency table of the scores obtained in a competition. Find the median score.
| Scores | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 11 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
Solution:
Number of scores = 11 + 9 + 5 + 10 + 15 = 50 (even number)
Since the number of scores is even, the median is at the average of the \(\left( \frac{n}{2} \right)^{th} = \left( \frac{50}{2} \right)^{th} = 25^{th}\) position and \(\left( \frac{n}{2} + 1\right)^{th} = 26^{th}\) position.
To find out the 25th position and 26th position, we add up the frequencies, to find the cumulative frequencies, as shown:
| Scores | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 11 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Cumulative Frequency | 11 + 0 = 11 | 11 + 9 = 20 | 20 + 5 = 25 | 25 + 10 = 35 | 35 + 15 = 50 |
The score at the 25th position is 2 and the score at the 26th position is 3.
The median is the average of the scores at 25th and 26th positions = \(\frac{2+3}{2} = 2.5\).
So the median is 2.5.
Videos
How To Find The Median From A Frequency Table (n is even)?
How to find the Mean, Median and Mode from a frequency distribution table?
Example:
The one hundred families in a particular neighborhood are asked their annual household income, to the
nearest $5 thousand dollars. The results are summarized in a frequency table. Find the median household
income.
How To Find The Median Of A Frequency Table (n is odd)?
How To Find The Mean, Mode And Median From A Frequency Distribution Table For Both Discrete And Grouped Data?
How To Estimate The Median, Quartiles From A Grouped Frequency Table Or Class Intervals?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.