Properties Of Integers
Related Pages
Integer Word Problems
Consecutive Integers 1
Consecutive Integers 2
More Algebra Word Problems
In these lessons and examples, we will learn about digits, integers, even and odd integers, operations on even and odd numbers, prime numbers and composite numbers. We will also learn the following properties of Integers: Commutative Property for Addition, Associative Property for Addition, Distributive Property, Identity Property for Addition, Identity Property for Multiplication, Inverse Property for Addition and Zero Property for Multiplication.
Introduction To Integer
Digits
Digits are the first concept of integers. There are ten digits namely: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
In our number system, the position of the digits are important. For example, consider the number 3,027. This can be represented in a place value table as follows:
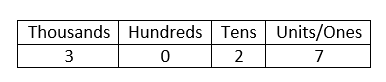
(For the SAT, the units digit and the ones digit refer to the same digit in a number).
Integers
Integers are like whole numbers but they also include negative numbers, for example, –4, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …
Positive integers are all the whole numbers greater than zero, ie: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … We say that its sign is positive.
Negative integers are the numbers less than zero, ie: –1, –2, –3, –4, –5, … We say that its sign is negative.
Integers extend infinitely in both positive and negative directions. This can be represented on the number line.
Zero is an integer that is neither positive nor negative.
Printable & Online Integers Worksheets
| Free Integer Games | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compare Integers | Integer Operations | Order of Operations |
| Add Integers | Subtract Integers | Integer Arithmetic |
| Multiply Integers | Divide Integers | |
Consecutive Integers
Consecutive integers are integers that follow in sequence, each number being 1 more than the previous number, for example 22, 23, 24, 25, …
Consecutive integers can be more generally represented by n, n +1, n + 2, n + 3, …, where n is any integer.
Even And Odd Integers
Even integers are integers that can be divided evenly by 2, for example, –4, –2, 0, 2, 4, … An even integer always ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8.
Zero is considered an even integer.
Odd integers are integers that cannot be divided evenly by 2, for example, –5, –3, –1, 1, 3, 5, … An odd integer always ends in 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9.
To tell whether an integer is even or odd, look at the digit in the ones place. That single digit will tell you whether the entire integer is odd or even. For example, the integer 3,255 is an odd integer because it ends in 5, an odd integer. Likewise, 702 is an even integer because it ends in 2.
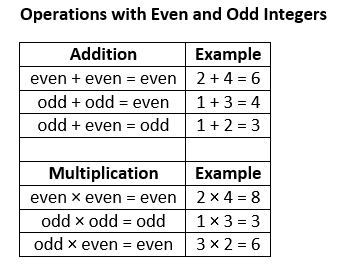
The following table shows the operations with even and odd integers.
Prime Numbers
A prime number is a positive integer that has exactly two factors, 1 and itself, for example 29 has exactly two factors which are 1 and 29. So 29 is a prime number.
On the other hand, 28 has six factors which are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28. So 28 is not a prime number. It is called a composite number. Some examples of prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, … Since the number 1 has only one factor (namely 1 itself), it is not a prime number.
The number 2 is the only prime that is even. Other even numbers will have 2 have as a factor and so will not be a prime.
A number that is not prime is called a composite number.
Properties Of Integers
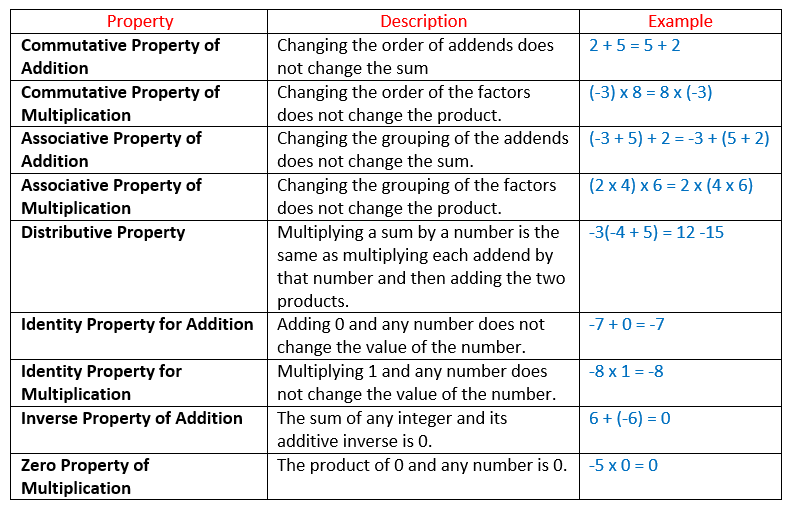
The following are some of the properties of integers. Scroll down the page for more examples and explanations of the different properties of integers.
Operations With Even And Odd Numbers
Add two even numbers and the result is even.
Add two odd numbers and the result is even.
Add one even and one odd and the result is odd.
Multiply two even numbers and the result is even.
Multiply two odd numbers and the result is odd.
Multiply one even and one odd and the result is even.
How To Distinguish Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a number greater than 1, which is only divisible by 1 and itself.
More Properties Of Integers
How to identify properties of Integers?
A property is a math rule that is always true.
Commutative Property for Addition, Associative Property for Addition, Distributive Property,
Identity Property for Addition, Identity Property for Multiplication, Inverse Property for
Addition and Zero Property for Multiplication.
Properties Of Integers
Three properties of integers are explained. Additive Identity, Additive Inverse, Opposite of a negative is positive. Examples are provided.
- Additive Identity: Adding 0 to any integer does not change the value of the integer.
- Additive Inverse: Each integer has an opposing number (opposite sign). When you add a number and its additive inverse, you get 0.
- The opposite of a negative is a positive.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.