Symmetry in Geometry
Related Pages
More Lessons for High School Geometry
Math Worksheets
A series of free, online High School Geometry Video Lessons.
Examples, solutions, videos, worksheets, and activities to help Geometry students.
In these lessons, we will learn
- reflectional symmetry/line symmetry
- rotational symmetry
- dilations
Symmetry in Geometry
Symmetry in geometry refers to a balanced and proportionate similarity that can be found in a shape or object. It means that parts of the object are identical or a mirror image of other parts, often allowing the object to remain unchanged after certain transformations.
Types of Symmetry in Geometry:
There are several types of symmetry, each defined by the transformation that leaves the object unchanged:
Reflectional Symmetry (or Line Symmetry)
Definition: A figure has reflectional symmetry if it can be divided by a line (the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry) into two halves that are mirror images of each other. If you fold the figure along this line, the two halves perfectly coincide.
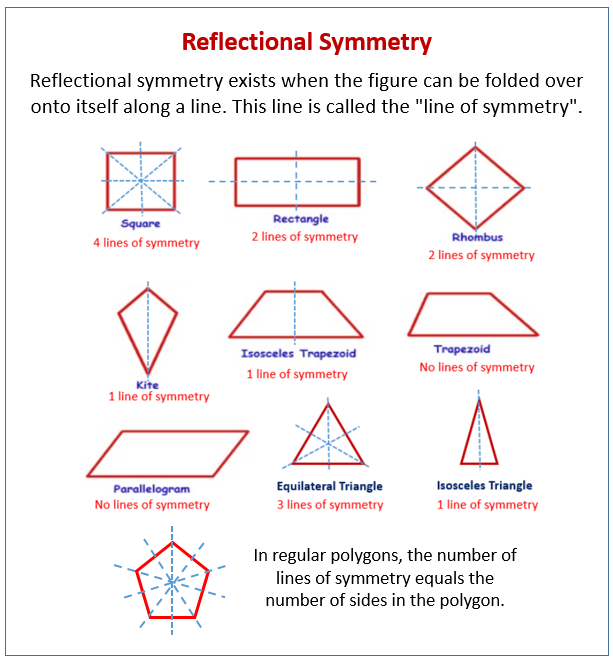
The following diagrams show the reflectional symmetry of some common shapes: square, rectangle, rhombus, kite, isosceles trapezoid, trapezoid, parallelogram, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, regular polygons. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on reflectional symmetry, rotational symmetry, and dilations.
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
Reflectional Symmetry
Symmetry in a figure exists if there is a reflection, rotation, or translation that can be performed and the image is identical. Reflectional symmetry exists when the figure can be folded over onto itself along a line. This line is called the “line of symmetry”. In regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry equals the number of sides in the polygon.
How to identify and describe reflectional symmetry?
An example of reflection symmetry
Looking at a few problems with more than one line of reflective symmetry
Rotational Symmetry
Symmetry in a figure exists if there is a reflection, rotation, or translation that can be performed and the image is identical. Rotational symmetry exists when the figure can be rotated and the image is identical to the original. Regular polygons have a degree of rotational symmetry equal to 360 divided by the number of sides.
How to define rotational symmetry and identify the degree of rotational symmetry of common regular polygons?
Rotational Symmetry, order of rotation and angle of rotation.
Dilations
A dilation is a non-rigid transformation, which means that the original and the image are not congruent. They are, however, similar figures. To perform dilations, a scale factor and a center of dilation are needed. If the scale factor is larger than 1, the image is larger than the original; if the scale factor is less than 1, the image is smaller than the original.
How to perform and describe a dilation.
Dilations. Basics and first part of an example.
Dilations. Second part of the example, and scalar multiplication of matrices.
Glide Reflection
A glide reflection is a composition of transformations. In a glide reflection, a translation is first performed on the figure, then it is reflected over a line. Therefore, the only required information is the translation rule and a line to reflect over. A common example of glide reflections is footsteps in the sand.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.