Transformation - Rotation, Reflection, Translation
Related Topics:
Common Core for Grade 8
Common Core for Mathematics
More Math Lessons for Grade 8
Examples, solutions, videos, and lessons to help Grade 8 students verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations.
A. Lines are taken to lines, and line segments to line segments of the same length.
B. Angles are taken to angles of the same measure.
C. Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines.
Common Core: 8.G.1
Suggested Learning Targets
*I can define and identify rotations, reflections, and translations.
*I can identify corresponding sides and corresponding angles of similar figures.
*I can understand prime notation to describe an image after a translation, reflection, or rotation.
*I can identify center of rotation.
*I can identify direction and degree of rotation.
*I can identify line of reflection.
*I can use physical models, transparencies, or geometry software to verify the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations (i.e. Lines are taken to lines and line segments to line segments of the same length, angles are taken to angles of the same measure, parallel lines are taken to parallel lines).
What is Transformation?
A mathematical transformation is a process that changes a geometric figure’s position, orientation (direction), or size. The original figure is called the pre-image, and the figure after the transformation is called the image. Transformations are fundamental in geometry and have applications in many areas, including computer graphics, art, engineering, and physics.
The following table shows examples of Transformations: Translation, Reflection, Rotation, and Dilation. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
Transformation Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets"
Printable & Online Transformation Worksheets
There are four main types of basic transformations, often studied in 2D (coordinate plane) geometry:
Translation (Slide), Rotation (Turn), Reflection (Flip), Dilation (Resizing - Enlargement or Reduction)
1. Translation (Slide)
A translation “slides” every point of a figure the same distance in the same direction.
It needs a translation vector or a description of the movement.
In coordinate geometry, if a point (x,y) is translated by a units horizontally and b units vertically, the image is (x+a,y+b).
Properties: It preserves size, shape, and orientation.
It is an isometry (or rigid transformation) because distances and angles are preserved.
There are no invariant points (points that remain unchanged).
2. Rotation (Turn)
A rotation “turns” a figure about a fixed point, called the center of rotation, through a specific angle of rotation in a specific direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise/anti-clockwise).
It needs a center of rotation, angle of rotation and direction of rotation.
Properties: It preserves size and shape, but the orientation changes.
It is an isometry.
The center of rotation is an invariant point.
3. Reflection (Flip)
A reflection “flips” a figure across a line called the line of reflection (or axis of symmetry). Each point in the image is the same distance from the line of reflection as the corresponding point in the pre-image, and the segment connecting a point to its image is perpendicular to the line of reflection.
It needs a line of reflection.
Properties: It preserves size and shape.
Reverses orientation: The figure appears as a “mirror image."
It is an isometry.
Points on the line of reflection are invariant points.
4. Dilation (Resizing)
A dilation changes the size of a figure but not its shape. The figure is enlarged or reduced.
It needs a center of dilation: The fixed point from which all distances are scaled.
Scale factor (k): The ratio of a distance in the image to the corresponding distance in the pre-image.
If |k|>1, it’s an enlargement.
If 0<|k|<1, it’s a reduction.
If k=1, the image is congruent to the pre-image (identity transformation).
If k<0, the image is on the opposite side of the center.
Properties: It preserves shape but not size.
It is not an isometry because distances are not preserved.
The center of dilation is an invariant point.
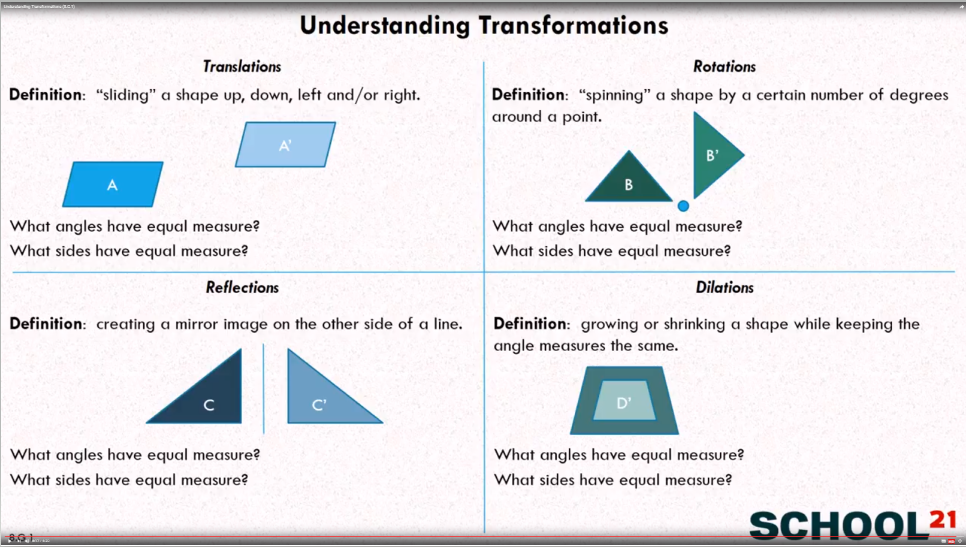
Understanding Transformations (8.G.1)
Translation: Sliding a shape up, down, left and/or right.
Reflection: Creating a mirror image on the other side of a line.
Rotation: Spinning a shape by a certain number of degrees around a point.
Dilation: Growing or shrinking a shape while keeping the angle measures the same.
Verify Properties of Transformations using Line Segments
Triangle Translation Construction of a Triangle Translation using patty paper.
Triangle Reflection
Construction of a Triangle Reflection using patty paper.
Performing a Rotation using Tracing Paper
This video shows show how to do a basic rotation using tracing paper. This rotation used (0,0) as the rotation point and rotated 90˚ clockwise.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.