Surface Area of Composite Figures - Prisms, Cones, Spheres, Pyramids
Related Topics:
More lessons for Grades 7 and 8 Math
More Geometry Lessons
Videos, worksheets, stories and songs to help Grade 7 and Grade 8 students learn how to find the surface area of composite figures that consist of prisms, cones, spheres, hemispheres, and pyramids.
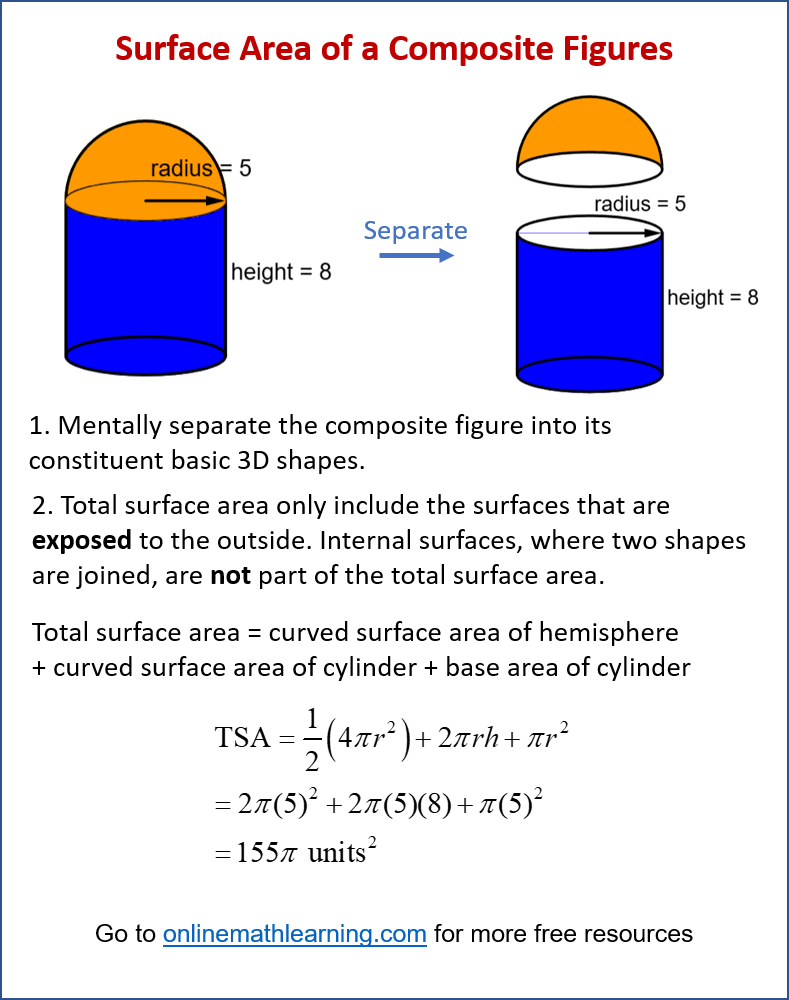
Surface Area of Composite Figures
Calculating the surface area of composite figures (also known as compound 3D shapes) involves combining the principles of finding the surface area of basic solid shapes, with an important consideration: you only account for the surfaces that are exposed to the outside.
Internal surfaces, where two shapes are joined, are not part of the total surface area.
The surface area of a composite figure is the sum of the areas of all its exposed surfaces.
The following diagram shows an example of how to calculate the surface area of a composite figure. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
Steps to Calculate the Surface Area of a Composite Figure:
-
Decompose the Figure (or Identify Subtracted Parts):
Mentally break the composite figure down into its constituent basic 3D shapes (e.g., a cylinder and a cone, two rectangular prisms, a prism with a hole).
Or, identify a larger shape from which a smaller shape has been removed. -
Identify Exposed Surfaces and Overlapping/Connecting Areas:
Determine which surfaces of each basic shape are actually part of the exterior of the composite figure.
Identify any areas where two shapes are joined. These connecting areas are not exposed and must not be included in the total surface area.
If a hole is cut out, the inside surface of that hole adds to the total surface area. -
Calculate the Area of Each Exposed Surface:
Use the standard surface area formulas for the basic shapes, but be mindful of only taking the exposed parts. -
Sum the Areas of All Exposed Surfaces:
Add up all the calculated areas of the external surfaces. -
State the Final Area with Units:
Always remember to include the appropriate square units
Surface Area of Composite Shapes
We take a look at how to find the overlapped area of composite shapes. Rectangular Prisms.
Volume and surface area composite figures (cylinder and hemisphere, cone, cylinder and hemisphere)
How to find surface area of composite objects?
Surface Area of Composite Figures (Prisms)
Learn to compute the surface area of composite figures. Triangular prism and rectangular prism.
Volume and Surface Area of Composite Figures (Spheres & Cones)
Learn to calculate the volume and surface area of composite figures.
Surface Areas of Composite Figures (Pyramids & Cones)
Learn to calculate surface area of composite figures.
Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones - Applications
Learn to apply surface areas of pyramids and cones to real life problems.
- A cone-shaped roof has a diameter of 12 feet and a height of 8 feet. If the roofing material comes in 120 square-foot rolls, how many rolls will be needed to cover this roof?
- The height of a pyramid is 216 feet and the side of the (square) base measures 346 feet. Find the lateral surface area.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.