Sine and Cosine Addition Formulas
Related Pages
Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric Ratios
Lessons On Trigonometry
Trigonometry Worksheets
Math Worksheets
A series of free, online Trigonometry Lessons with videos, solutions, examples, worksheets, and activities to help Trigonometry students.
In this lesson, we will learn
- the cosine addition formula
- how to derive the cosine of a sum and difference of two angles
- the sine addition formula
- how to derive the sine of a sum and difference of two angles
- how to use the sine and cosine addition and subtraction formulas to prove identities
- how to use the sine and cosine addition and subtraction formulas to determine function values.
The following diagram gives the sine and cosine addition and subtraction formulas. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
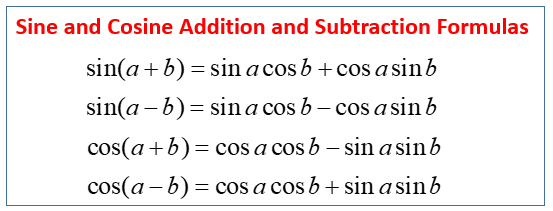
Trigonometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Trigonometry worksheets:
Printable & Online Trigonometry Worksheets
How to remember the formulas?
Sine: The sine formulas follow a pattern of “sin cos” and “cos sin”. The sign in the formula matches the sign between the angles (plus stays plus, minus stays minus).
Cosine: The cosine formulas follow a pattern of “cos cos” and “sin sin”. The sign in the formula is the opposite of the sign between the angles (plus becomes minus, minus becomes plus).
Cosine Addition Formula
The cosine addition formula calculates the cosine of an angle that is either the sum or difference of two other angles. It arises from the law of cosines and the distance formula. By using the cosine addition formula, the cosine of both the sum and difference of two angles can be found with the two angles’ sines and cosines.
This video shows the formula for deriving the cosine of a sum of two angles.
cos(A + B) = cosAcosB − sinAsinB
We will use the unit circle definitions for sine and cosine, the Pythagorean identity, the distance formula.
How to derive the cosine of a difference formula?
A proof that cos (A − B) = cosAcosB + sinAsinB.
The main idea is to create a triangle whose angle is a difference of two other angles, whose adjacent
sides, out of simplicity, are both 1. By using both the distance formula and the law of cosines,
we can get an equation where cos(A − B) is present.
Sine Addition Formula
Starting with the cofunction identities, the sine addition formula is derived by applying the cosine difference formula.
There are two main differences from the cosine formula:
- the sine addition formula adds both terms, where the cosine addition formula subtracts and the subtraction formula adds; and
- the sine formulas have sin-sin and cos-cos.
Both formulas find values for angles.
How to derive the sine of a sum formula?
We will use the cofunction identities and the cosine of a difference formula.
sin(A + B) = sinAcosB + cosAsinB
The derivation of the sum and difference identities for cosine and sine.
cos(A + B) = cosAcosB − sinAsinB
cos (A − B) = cosAcosB + sinAsinB
sin(A + B) = sinAcosB + cosAsinB
sin(A − B) = sinAcosB − cosAsinB
Using the Sine and Cosine Addition and Subtraction Formulas to Prove Identities
Applying the cosine addition and sine addition formulas to prove the cofunction identities, add π and supplementary angle identities.
Using the formulas,
we see that sin(π/2-x) = cos(x), cos(π/2-x) = sin(x);
that sin(x + π) = −sin(x), cos(x + π) = −cos(x);
and that sin(π − x) = sin(x), cos(π − x) = −cos(x).
The formulas also give the tangent of a difference formula, for tan(alpha − beta).
How to use the sine and cosine addition formulas to prove the cofunction identities?
In this video, we will verify a Trig identity by using the basic identities and the identity for
the cosine of a sum or difference.
We prove that (cos(x+y))/(cos(x − y)) = (cot y − tan x)/(cot y + tan x) using a trig proof.
Using the Sine and Cosine Addition and Subtraction Formulas to determine function values
This video provides an example of using the sine sum and difference identity to determine a sine function value.
Determine the exact value of sin(105 degrees) using the sum and difference identity.
This video provides an example of using the cosine sum and difference identity to determine a cosine function value.
Determine the exact value of cos(13/12π) using the sum and difference identity.
Use the sum and difference identities for sine to determine the function values.
Determine sin(A − B), given sin A = 4/5 in quadrant II and cos B = −5/13 in quadrant III.
Use the sum and difference identities for cosine to determine the function values.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.