Similarity, Area Ratios and Volume Ratios
Related Pages
More Lessons for Grade 8 Math
Math Worksheets
These lessons, with videos, examples and step-by-step solutions,will help Grade 8 students learn how to convert between length and area ratios of similar polygons and how to identify if two solids are similar and how to convert length ratios to surface area and volume ratios.
Similar Shapes
When two geometric shapes are similar, it means they have the exact same shape but potentially different sizes. One is an enlargement or reduction of the other.
For two shapes to be similar:
Corresponding angles must be equal.
Corresponding linear dimensions (sides, radii, heights, diameters, etc.) must be in proportion. This constant ratio is called the linear scale factor.
These properties lead to specific relationships between their areas and volumes.
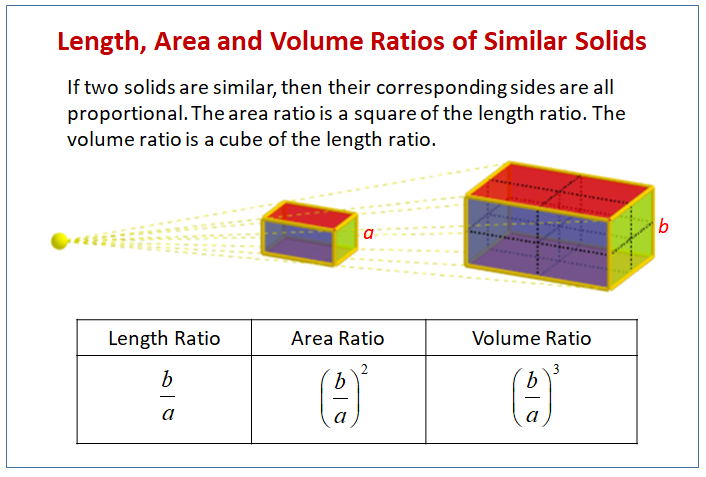
The following diagram shows how to convert between length, area and volume ratios of similar solids. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions length, area and volume of similar figures.
Algebra Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Algebra worksheets:
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
1. Linear Ratio (Scale Factor, k)
If we have two similar shapes, say Shape 1 and Shape 2, and we choose corresponding linear dimensions (e.g., side length, radius, height), their ratio is the linear scale factor, often denoted as k
\(\frac{\text{Length}_1}{\text{Length}_2} = k \)
2. Area Ratio (Square of Scale Factor)
Since area is two-dimensional, the ratio of areas is the square of the scale factor:
\(\frac{\text{Area}_1}{\text{Area}_2} = k^2 \)
3. Volume Ratio (Cube of Scale Factor)
Since volume is three-dimensional, the ratio of volumes is the cube of the scale factor:
\(\frac{\text{Volume}_1}{\text{Volume}_2} = k^3 \)
Similarity and Area Ratios
Is there any relationship between the ratio of the areas of two similar figures?
If two triangles are similar, then their corresponding sides are proportional. Since sides are a length and lengths are one dimensional, the side ratio will not predict the ratio of the areas. To find the area ratios, raise the side length ratio to the second power. This applies because area is a square or two-dimensional property.
Similarity and Volume Ratios
How are the ratios of the surface area of solids related to their corresponding volumes?
If two solids are similar, then their corresponding sides are all proportional. The ratio of their surface areas is the side ratio squared and note that the ratios of the areas does not give the actual surface areas. The volume ratio for the two solids is the side length ratio raised to the third power. Again, this is not the solids’ volume, only the ratio of the volumes.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.