Reflection Transformation
Related Pages
Properties Of Reflection
Transformation
More Lessons On Geometry
In this lesson, we will learn
- what is reflection?
- how to draw the reflected image of an object (drawn on grid lines) given the line of reflection.
- how to draw the reflected image of an object (using a compass or ruler) given the line of reflection.
- how to reflect points and shapes on the coordinate plane using the Coordinate Rules.
- how to reflect an object using a transformation matrix.
What is Reflection?
A reflection transformation, in geometry, is a type of transformation that flips a figure or shape across a line, creating a mirror image. This line is called the line of reflection or the axis of reflection.
Example:
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Geometry worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
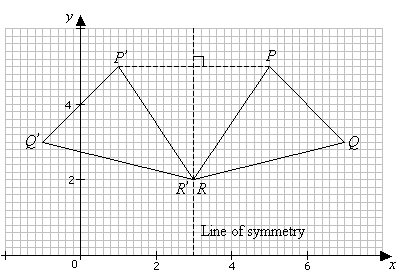
A reflection is defined by the axis of symmetry or mirror line. In the above diagram,
the mirror line is x = 3.
The line of reflection is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining any point and its
image (e.g. PP ’ in the above figure).
All the points on the mirror line are not changed. These points are said to be invariant.
(R is an invariant point in the above.)
Properties of Reflection:
- A reflection maps every point of a pre-image (the original figure) to a corresponding point on the image (the new figure) such that:
- The line of reflection is the perpendicular bisector of the segment connecting the pre-image point and its image point. This means the line cuts the segment in half at a 90-degree angle.
- The distance from any point on the pre-image to the line of reflection is equal to the distance from its corresponding image point to the line of reflection.
- The image produced by a reflection is always congruent to the pre-image. This means it has the same size and shape. This type of transformation is called isometric transformation.
- Orientation Reversal: The orientation of the figures is laterally inverted, that is they are facing opposite directions. Think of it like looking in a mirror – your left side appears on the right side of your reflection, and vice versa.
- Fixed Points: Any point that lies on the line of reflection remains unchanged (it is its own image).
Drawing The Image on Grid Lines
If the axis of reflection is on one of the grid lines, we just count the number of squares from a point on the object to the axis and the image is the same distance from the axis.
Example:
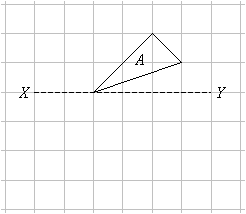
In the diagram, the figure A is reflected in the line XY. Draw the image of A in the diagram.
Solution:
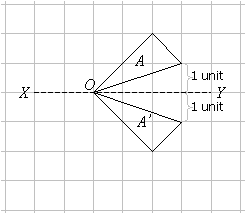
Note that the point O remained unchanged under reflection because it is on the axis of reflection. Any point on the line of reflection is unchanged – such points are described as invariant.
How to reflect a shape on squared paper without using tracing paper
This video shows how to reflect a shape on squared paper without using tracing paper. Just
count the distance of each corner to the mirror line and count the same distance away from
the mirror line. Once all the points have been reflected them, join the points up neatly
using your ruler.
Draw the image using a compass
If the axis of reflection is not on the grid lines, we will need to use a compass to construct the image.
Example:
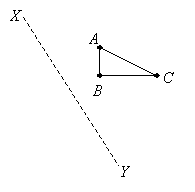
In the diagram below, the triangle ABC is reflected in the line XY. Draw the image of the triangle in the diagram.
Solution:
Step 1: Place the sharp point of a compass at A and draw two
arcs intersecting the line XY

Step 2: Place the sharp point of the compass on the first intersecting point and mark an arc on the opposite side of XY. Place the sharp point of the compass on the second intersecting point and mark an arc to intersect with the first arc. The intersection is the image of A’.
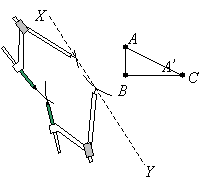
Step 3: Repeat steps 1 and 2 to get the points B ’ and C ’. Join the points A ’ , B ’ and C ’ to get the image A ’ B ’ C ’.

Construct Reflection by Hand
How to reflect a figure over a line by hand using a ruler.
How to construct a Line of Reflection?
Construct a line of reflection given the object and the image.
Reflection on the Coordinate Plane
We will now look at how points and shapes are reflected on the coordinate plane. It will be helpful to note the patterns of the coordinates when the points are reflected over different lines of reflection.
Coordinate Rules for Reflection
If (a, b) is reflected on the x-axis, its image is the point (a, -b)
If (a, b) is reflected on the y-axis, its image is the point (-a, b)
If (a, b) is reflected on the line y = x, its image is the point (b, a)
If (a, b) is reflected on the line y = -x, its image is the point (-b, a)
Geometry Reflection
A reflection is an isometry, which means the original and image are congruent, that can be
described as a “flip”. To perform a geometry reflection, a line of reflection is needed;
the resulting orientation of the two figures are opposite. Corresponding parts of the
figures are the same distance from the line of reflection. Ordered pair rules reflect over
the x-axis: (x, -y), y-axis: (-x, y), line y = x: (y, x).
This video shows reflection over the x-axis, y-axis, x = 2, y = −2
This video shows reflection over y = x, y = − x. A reflection that results in an overlapping shape.
This video shows reflection over the x-axis, y-axis, x = −3, y = 5, y = x, and y = − x.
Reflections using Matrices
This lesson involves reflections in the coordinate plane. We use coordinate rules as well as matrix multiplication to reflect a polygon (or polygon matrix) about the x-axis, y-axis, the line y = x or the line y = -x.
Matrices and Reflections
Performing reflections with matrices over the y-axis and x-axis.
Matrices for Reflections over the y-axis and x-axis.
Matrices for Reflections over the line y = x.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.