Reference Angle
More Lessons for Trigonometry
Math Worksheets
In this lesson, we will look into how to use the reference angle to find the sine, cosine and tangent of non-acute angles.
What is a reference angle?
A reference angle is the acute angle formed by the terminal side of the given angle and the x-axis.
How to find the reference angle?
Step 1: Sketch the given angle
Step 2: Drop a perpendicular to the x-axis
Step 3: Determine the angle measure of the triangle formed
How to use reference angles to find the sine, cosine and tangent of non-acute angles?
To find the value of sine, cosine and tangent at non-acute angles (from 90 to 360), first draw the angle on the unit circle and find the reference angle.
A reference angle is formed by the terminal side and the x-axis and will therefore always be acute.
When evaluating sine, cosine and tangent for the reference angle, determine if each value is positive or negative by identifying the quadrant the terminal side is in. The Cartesian plane is divided into 4 quadrants by the two coordinate axes. These 4 quadrants are labeled I, II, III and IV respectively.

We want to consider how to evaluate the trigonometric ratios of angles in the four quadrants. When evaluating the trigonometric ratios of non-acute angles, we need to consider the concept of reference angles.
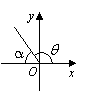
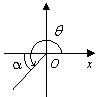
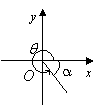
The table below shows the reference angle, α , in quadrant I which corresponds to the angle, θ , in quadrants II, III, and IV.
Quadrant |
Angle θ |
Reference angle α |
Diagram |
II |
90˚ < θ < 180 ˚ |
α = 180 ˚ – θ |
|
III |
180˚ < θ < 270 ˚ |
α = θ – 180˚ |
|
IV |
270˚ < θ < 360 ˚ |
α = 360 ˚ – θ |
|
Determine the reference angle that corresponds to each of the following angle.
a) 165˚
b) 249˚
c) 328˚
a) 165˚ is in quadrant II (90˚ < 165˚ < 180˚ )
The reference angle is 180˚ – 165˚ = 15˚
b) 249˚ is in quadrant III (180˚ < 249˚ < 270˚ )
The reference angle is 249˚ – 180˚ = 69˚
c) 328˚ is in quadrant III (270˚ < 328˚ < 360˚ )
The reference angle is 360˚ – 328˚ = 32˚
What are reference angles are and how to find them, and then how to use them to determine the sine and cosine values of angles greater than ninety degrees?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.