Poisson Distribution
Related Pages
Statistics: Poisson Distribution/Process
Probability Distributions
Statistics Lessons
In these lessons we will learn about the Poisson distribution and its applications.
What Is Poisson Distribution?
The Poisson Distribution is a discrete distribution. It is named after Simeon-Denis Poisson (1781-1840), a French mathematician, who published its essentials in a paper in 1837. The Poisson distribution and the binomial distribution have some similarities, but also several differences.
The binomial distribution describes a distribution of two possible outcomes designated as successes and failures from a given number of trials. The Poisson distribution focuses only on the number of discrete occurrences over some interval. A Poisson experiment does not have a given have a given number of trials (n) as binomial experiment does. For example, whereas a binomial experiment might be used to determine how many black cars are in a random sample of 50 cars, a Poisson experiment might focus on the number of cars randomly arriving at a car wash during a 20-minute interval.
The Poisson distribution has the following characteristics:
- It is a discrete distribution.
- Each occurrence is independent of the other occurrences.
- It describes discrete occurrences over an interval.
- The occurrences in each interval can range from zero to infinity.
- The mean number of occurrences must be constant throughout the experiment.
What Is The Poisson Distribution Formula?
The Poisson distribution is characterized by lambda, λ, the mean number of occurrences in the interval. If a Poisson-distributed phenomenon is studied over a long period of time, λ is the long-run average of the process. The Poisson formula is used to compute the probability of occurrences over an interval for a given lambda value.
The following diagram gives the Poisson Formula. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions on how to use the Poisson Distribution Formula.
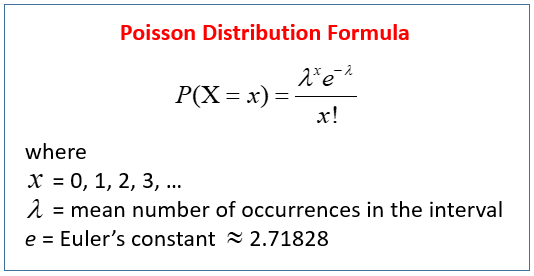
The probability of observing ‘k’ events in a given interval is calculated using the following formula:
P(X = k) = (λk e(-λ))/k!
Where:
P(X = k) is the probability of k events occurring.
λ (lambda) is the average number of events.
e is Euler’s number (approximately 2.71828).
k! is the factorial of k.
How To Derive The Poisson Formula From The Binomial Formula?
Introduction to Poisson Processes and the Poisson Distribution.
More Of The Derivation Of The Poisson Distribution
The Poisson Distribution
The following video will discuss a situation that can be modeled by a Poisson Distribution, give the formula, and do a simple example illustrating the Poisson Distribution.
Example:
Suppose a fast food restaurant can expect two customers every 3 minutes, on average. What is
the probability that four or fewer patrons will enter the restaurant in a 9 minute period?
An Introduction To The Poisson Distribution
What are the conditions required for a random variable to have a Poisson distribution?
Suppose we are counting the number of occurrences of an event in a given unit of time, distance, area or volume. For example, the number of car accidents in a day or the number of dandelions in a square meter plot of land. If the events occur independently and the probability of an event occurs in a given length of time and does not change through time then X, the number of events in a fixed unit of time, has a Poisson distribution.
Example:
One nanogram of Plutonium-239 will have an average of 2.3 radioactive decays per second, and
the number of decays will follow a Poisson distribution.
What is the probability that in a 2 second period there are exactly 3 radioactive decays?
What is the relationship between the binomial distribution and the Poisson distributions?
The binomial distribution tends toward the Poisson distribution as n → ∞, p → 0 and np stays constant.
The Poisson distribution with λ = np closely approximates the binomial distribution if n is large and p is small. The Poisson distribution is typically used as an approximation to the true underlying reality. It can be difficult to determine whether a random variable has a Poisson distribution.
Statistics: Introduction To The Poisson Distribution
In this video, we discuss the basic characteristics of the Poisson Distribution using a real-world example involving a checkout line at a supermarket. A basic understanding of the binomial distribution is helpful, but not necessary. It will also show you how to calculate Poisson probabilities on at TI calculator.
Example:
Let’s say you are a cashier at Wal-Mart. It is 4:30pm and your shift ends at 5:00pm. The store
policy is to close your checkout line 15 minutes before your shift ends (in this case 4:45) so
that you van finish checking-out the customers already in your line and leave on-time.
By examining overhead cameras, store data indicates that between 4:30pm and 4:45pm each weekday,
an average of 10 customers enter any given checkout line.
What is the probability that exactly 7 customers enter your line between 4:30 and 4:45? What
is the probability that more than 10 people arrive? (Which means you will probably be on shift
later than 5:00pm)
Poisson Characteristics
- Discrete outcomes
- The number of occurrences in each interval can range from zero to infinity (theoretically)
- Describes the distribution of infrequent (rare) events
- Each event is independent of the other events
- Describes discrete events over an interval
- Expected number of occurrences E(X) are assumed to be constant throughout the experiment.
Statistics: Poisson Practice Problems
This video goes through two practice problems involving the Poisson Distribution. The first problem examines customer arrivals to a bank ATM and the second analyzes deer-strike probabilities along sections of a rural highway. You are assumed to have a basic understanding of the Poisson Distribution.
Example 1:
A bank is interested in studying the number of people who use the ATM located outside its
office late at night.
On average, 1.6 customers walk up to the ATM during any 10 minute interval between 9pm and
midnight.
What is lambda λ for this problem?
What is the probability of exactly 3 customers using th ATM during any 10 minute interval?
What is the probability of 3 or fewer people?
Example 2:
The Indiana Department of Transportation is concerned about the number of deer being struck by
cars between Martinsville and Bloomington. They note the number of deer carcasses and other
deer-related accidents over a 1-month period in a 2-mile intervals. What is the probability of
zero deer strike incidents during any 2-mile interval between Martinsville and Bloomington?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.