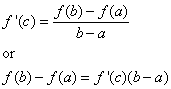Mean Value Theorem
More Lessons for Calculus
Math Worksheets
Definition of the Mean Value Theorem
The following diagram shows the Mean Value Theorem. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the Mean Value Theorem.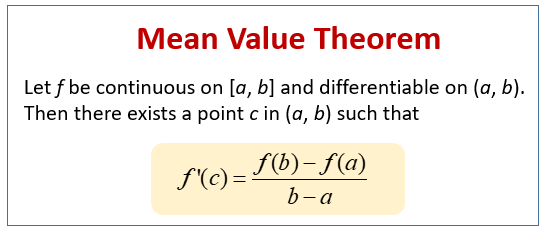
Let f be a function that satisfies the following hypotheses:
- f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]
- f is differentiable on the open interval (a, b)
Then there is a number c in (a, b) such that
How to use the Mean Value Theorem?
Example:
Given f(x) = x3 – x, a = 0 and b = 2. Use the Mean Value Theorem to find c.
Solution:
Since f is a polynomial, it is continuous and differentiable for all x, so it is certainly continuous on [0, 2] and differentiable on (0, 2).
By the Mean Value Theorem, there is a number c in (0, 2) such that
f(2) – f(0) = f ’(c) (2 – 0)
We work out that f(2) = 6, f(0) = 0 and f ‘(x) = 3x2 – 1
We get the equation
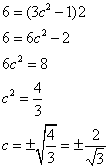
But c must lie in (0, 2) so ![]()
Introduction into the mean value theorem.
Examples and practice problems that show you how to find the value of c in the closed interval [a,b] that satisfies the mean value theorem. For the mean value theorem to be applied to a function, you need to make sure the function is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b).
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.