Line Symmetry And Plane Symmetry
Related Pages
Lines Of Symmetry
Rotational Symmetry
Polygons & Symmetry
More Geometry Lessons
These lessons help Geometry students learn about line symmetry and plane symmetry, with video lessons, examples and solutions.
Line Symmetry
Line symmetry, also known as reflectional symmetry or mirror symmetry, is a property of a shape or object where it can be divided by a straight line into two halves that are mirror images of each other.
Imagine folding the shape along that line; if the two halves perfectly match up, then the shape has line symmetry, and that fold line is called the line of symmetry (or axis of symmetry).
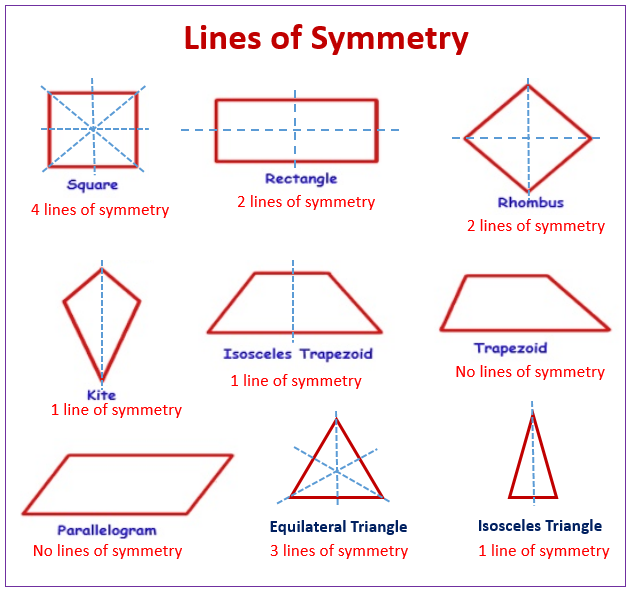
The following diagram shows the line of symmetry for quadrilaterals and triangles. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on lines of symmetry.
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Polygons & Symmetry Worksheets
How to Identify Line Symmetry:
- The Fold Test: Mentally (or physically) try to fold the shape in half. If you can find a way to fold it so that one half perfectly covers the other, it has line symmetry. The fold line is the line of symmetry.
- The Mirror Test: Imagine placing a small mirror on the shape. If the reflection in the mirror completes the other half of the original shape, then the line where the mirror is placed is a line of symmetry.
Examples of Shapes with Line Symmetry:
Many common geometric shapes and objects exhibit line symmetry:
Square: Has 4 lines of symmetry (two horizontal/vertical, two diagonal)
Rectangle: Has 2 lines of symmetry (one horizontal, one vertical, through the midpoints).
Equilateral Triangle: Has 3 lines of symmetry (from each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side).
Isosceles Triangle: Has 1 line of symmetry (from the vertex angle to the midpoint of the base).
Circle: Has an infinite number of lines of symmetry (any line passing through its center).
Examples of Shapes Without Line Symmetry:
Scalene Triangle: All sides and angles are different.
Parallelogram: (Unless it’s a rectangle or a rhombus, which are special parallelograms).
Plane Symmetry
In geometry, plane symmetry is a property of a three-dimensional (3D) object or figure where it can be divided by an imaginary flat surface (a plane) into two halves that are exact mirror images of each other.
How to Identify Plane Symmetry:
- The “Slicing” Test: Imagine taking a knife and slicing through the 3D object. If you can make a cut such that the two pieces created are perfect mirror images of each other, then the plane of that cut is a plane of symmetry.
- Visualizing Reflection: Mentally reflect one half of the object across the proposed plane. If the reflected half perfectly superimposes on the other half of the original object, it’s a plane of symmetry.
Videos
Reflection Symmetry (or Line Symmetry) and Rotational Symmetry
Symmetry in a figure exists if there is a reflection, rotation, or translation that can be performed and the image is identical. Reflectional symmetry exists when the figure can be folded over onto itself along a line. This line is called the “line of symmetry”. In regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry equals the number of sides in the polygon.
Line Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
Learn to identify lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry
Plane Symmetry
Plane symmetry is analogous to line symmetry, except that it is in three dimensions. The three dimensional figure is divided into two halves by a plane.
The following diagram shows the planes of symmetry of a cuboid or rectangular solid.
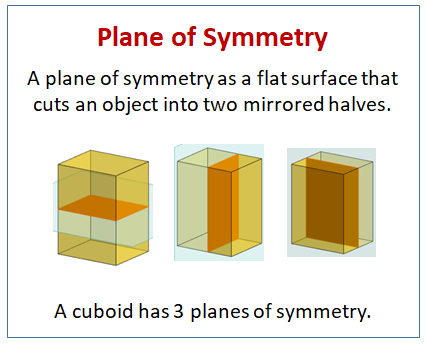
Plane symmetry and axis symmetry
Examples of plane symmetry and axis symmetry
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.