Inverse Sine, Cosine and Tangent
Related Topics:
More Lessons for Trigonometry
Math Worksheets
A series of free, online Trigonometry Video Lessons.
Example, solutions, videos, worksheets, and activities to help Trigonometry students.
In this lesson, we will learn
- the inverse sine function and its graph
- the inverse cosine function and its graph
- the inverse tangent function and its graph
- how to evaluate inverse trigonometric expressions
Graphing Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Graphing inverse trigonometric functions involves understanding the concept of inverse functions and the restricted domains of the original trigonometric functions.
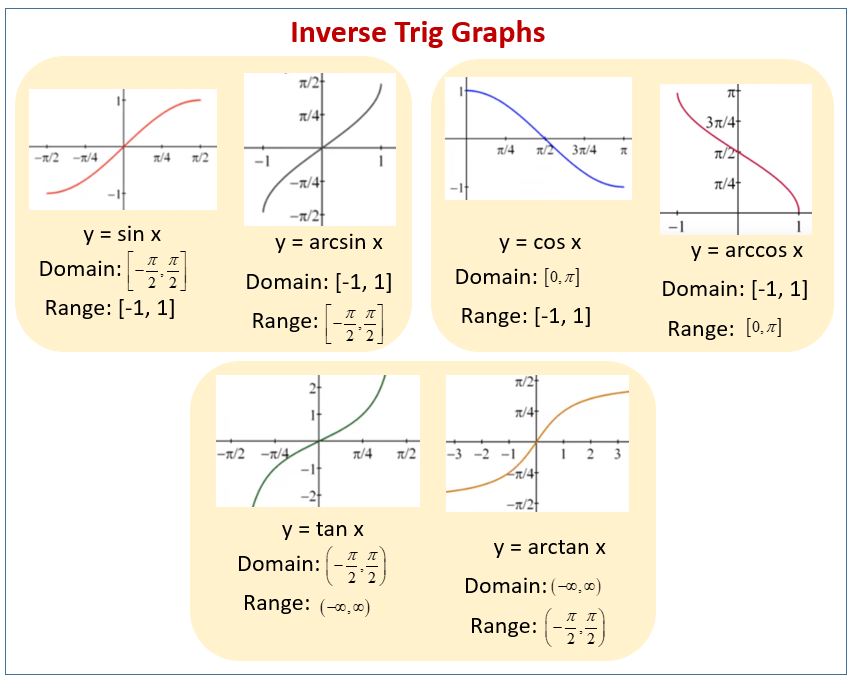
The following diagram shows examples of inverse sine, cosine, tangent functions and their graphs. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on Inverse Trigonometric functions.
Trigonometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Trigonometry Worksheets
Inverse Functions
An inverse function “undoes” the original function. If (a,b) is a point on the graph of a function y = f(x), then (b,a) is a point on the graph of its inverse y = f−1(x). Graphically, this means the graph of an inverse function is a reflection of the original function’s graph across the line y=x.
Restricted Domains
Trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, etc.) are periodic, meaning their graphs repeat infinitely. This makes them not one-to-one (they fail the horizontal line test). For an inverse function to exist and also be a function, the original function must be one-to-one. To achieve this, we restrict the domain of the original trigonometric functions to an interval where they are one-to-one and cover their entire range.
Introduction to Inverse Sine, Inverse Cosine, and Inverse Tangent
Inverse Sine Function
Since sine is not a one-to-one function, the domain must be limited to − π/2 to π/2, which is called the restricted sine function.
The inverse sine function is written as sin−1(x) or arcsin(x).
Inverse functions swap x- and y-values, so the range of inverse sine is − π/2 to π/2 and the domain is −1 to 1.
When evaluating problems, use identities or start from the inside function.
How to restrict the domain of sine so it will have an inverse function?
How to graph the inverse sine function
Inverse Cosine Function
Since cosine is not a one-to-one function, the domain must be limited to 0 to π, which is called the restricted cosine function. The inverse cosine function is written as cos−1(x) or arccos(x). Inverse functions swap x- and y-values, so the range of inverse cosine is 0 to π and the domain is −1 to 1. When evaluating problems, use identities or start from the inside function.
How to restrict the domain of cosine so it will have an inverse function.
Inverse Tangent Function
Since tangent is not a one-to-one function, the domain must be limited to − π/2 to π/2, which is called the restricted tangent function. The graph of the inverse tangent function is a reflection of the restricted tangent function over y = x. Note that the vertical asymptotes become horizontal, at y = π/2 and y = − π/2, and the domain and ranges swap for the inverse function.
How to restrict the domain of tangent so it will have an inverse function.
Introduction to the inverse functions of sine, cosine, and tangent
Define the inverse functions of sine, cosine, and tangent
Graph the inverse functions of sine, cosine, and tangent
Use inverse trigonometric functions to solve functions
Using the Inverse Trigonometric Functions
In a problem where two trig functions are not inverses of each other (also known as “inverse trigonometric functions”),
(1) replace the inverse function with a variable (which represents an angle),
(2) use the definition of the inverse function to draw the angle in the unit circle and identify one coordinate,
(3) find the missing coordinate (use Pythagorean Theorem, for example),
(4) use the coordinates to find the missing value.
This video provides examples of evaluating inverse trigonometric expressions using the unit circle.
This video provides examples of evaluating inverse trigonometric expressions using reference triangles.
This video provides examples of evaluating inverse trigonometric expressions using the unit circle. inverse cosecant, inverse secant, inverse cotangent.
This video provides and example of how to evaluate a trigonometric expression containing an inverse trigonometric function.
tan(sin−1(−12/13))
sin(arctan(−7))
sin(tan−1(u/3))
This video provides examples of simplifying expressions with inverse trig functions and trig functions.
sin(sin−1(2/5)) , cos(cos−1(−2/7)), tan(cos−1(2/3))
This video provides examples of simplifying expressions with inverse trig functions and trig functions.
sin−1(sin(π/3)), sin−1(cos(−3π/4)), tan−1(sin(−π/6))
How to evaluate expressions like tan(sin−1(4/5))?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.