Graphing Rational Functions
Related Topics:
More Lessons for PreCalculus
Math Worksheets
Examples, solutions, videos, worksheets, and activities to help students learn about how to graph rational functions.
What is a Rational Function?
A rational function is of the form
\(f(x) = \frac{p(x)}{q(x)}\) where \(p(x)\) and \(q(x)\) are polynomials and \(q(x) ≠ 0\).
Graphing them involves identifying key features like asymptotes, intercepts, and behavior at critical points.
The following diagram shows how to graph rational functions of the form \(y = \frac{(ax + b)}{(cx + d)}\). Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to graph rational functions.
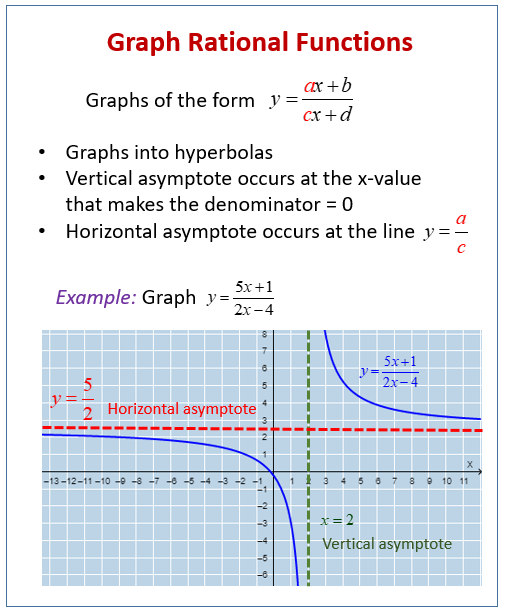
How to graph rational functions?
I. Graph rational functions of the form:
\(y = \frac{(ax + b)}{(cx + d)}\)
- Graphs into hyperbolas
- Vertical asymptote occurs at the x value that makes the denominator = 0.
- Horizontal asymptote occurs at the line \(y = \frac{a}{c}\).
II. Graph rational functions of the form:
\(f(x) = \frac{p(x)}{q(x)}\) where \(p(x)\) and \(q(x)\) are polynomials.
Step 1: Simplify the Function (if possible)
Factor the numerator and denominator to check for holes (common factors).
Example:
\(f(x)=\frac{(x-2)(x+1)}{(x-2)(x-3)}\implies \) Hole at \(x=2\)
(Cancel \((x-2)\) but note \(x ≠2\))
Step 2: Find Vertical Asymptotes (VA)
Set the denominator = 0 (after simplifying).
Example:
\(f(x)=\frac{(x+1)}{(x-3)}\implies \) VA at \(x=3\)
Step 3: Find Horizontal/Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes (HA)
Horizontal Asymptote (HA): Compare degrees of numerator (n) and denominator (d):
If n < d: HA at y = 0 (the x-axis).
If n = d: HA at \(y=\frac{\text{leading coefficient of p(x)}}{\text{leading coefficient of q(x)}}\)
If n > d: No HA (but possibly a slant asymptote)
Slant Asymptote (SA): If n = d + 1, perform polynomial long division. The quotient (ignoring the remainder) is the equation of the slant asymptote.
Step 4: Find x- and y-Intercepts
Step 5: Determine Behavior Near Asymptotes
Vertical Asymptote (VA): Check left/right limits.
Horizontal Asymptote (HA): Check end behavior.
Step 6: Sketch the Graph
Draw all asymptotes (vertical, horizontal, or slant) as dashed lines.
Plot all intercepts (x- and y-).
Plot any holes as open circles.
Use the information from step 5 to draw the branches of the graph.
Draw smooth curves connecting your plotted points and respecting the behavior near asymptotes.
Videos
Rational Functions and their Graphs
Learn about rational functions and their graphs
Graphing a Rational Function - Example 1
Graphing a Rational Function - Example 2
Graphing a Rational Function - Example 3
Graphing a Rational Function - Example 4
Graphing Rational Functions
A couple of examples on graphing rational functions.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.