GCF & LCM (Grade 6)
Related Topics:
Common Core for Grade 6
More Lessons for Grade 6
GCF & Distributive Property
Videos, solutions, and lessons to help Grade 6 students learn to find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12.
Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. For example, express 36 + 8 as 4(9 + 2).
Common Core: 6.NS.4
Suggested Learning Targets
- I can find the greatest common factor and least common multiple.
I can identify the factors of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and determine the Greatest Common Factor. - I can identify the multiples of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12 and determine the Least Common Multiple.
- I can use the distributive property for whole numbers with no common factor.
Component Skills from Previous Grades
| 3.OA.5 Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. For example, write 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) |
Students should be comfortable with the concepts of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and/or division. |
| How to find GCF & LCM? | ||
|---|---|---|
| GCF | LCM | Math Worksheets |
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The following diagrams show how to find the Greatest Common Factor using the List Method, Prime Factorization (Factor Tree) Method and Repeated Division (Ladder) Method. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
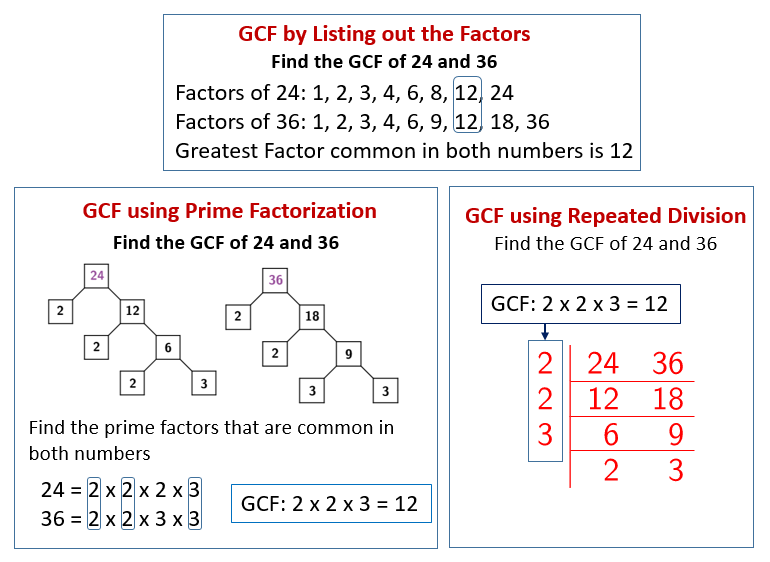
Finding the GCF or Greatest Common Factor (6-NS-B-4)
Finding GCF or Greatest Common Factor by finding and comparing all the factors of two numbers.
6NS4-Greatest Common Factor Part 1
Factor Tree Method, List Method.
6NS4-Greatest Common Factor Part 2
Factor Tree Method, List Method.
Finding the GCF, Prime Factorization (6-NS-B-4)
This is a video of finding GCF by using the prime factorization method.
Finding the GCF using prime factorization.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The following diagrams show how to find the Least Common Multiple using the List Method, Prime Factorization (Factor Tree) Method and Repeated Division (Ladder) Method. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
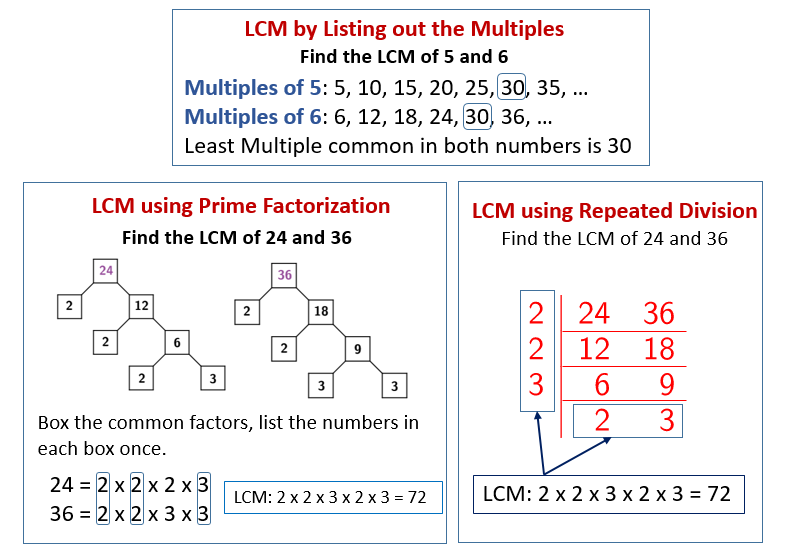
6NS4-Least Common Multiple.
Prime Factorization to Find the LCM
Break down the numbers into factors of all primes, then take the highest power of each different prime number from both your prime factorizations. Multiply them together, and you’ve now got the LCM/LCD for your original numbers.
Finding the LCM using the “Ladder” Method.
GCF & Distributive Property
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.