Conic Sections - Circles
Related Pages
Conic Sections: Circles 2
Conic Sections: Ellipses
Conic Sections: Parabolas
Conic Sections: Hyperbolas
A series of free, online video lessons with examples and solutions to help Algebra students learn about circle conic sections.
What is the equation of circle?
The following diagram shows how to derive the equation of circle (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 using Pythagorean Theorem and distance formula. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
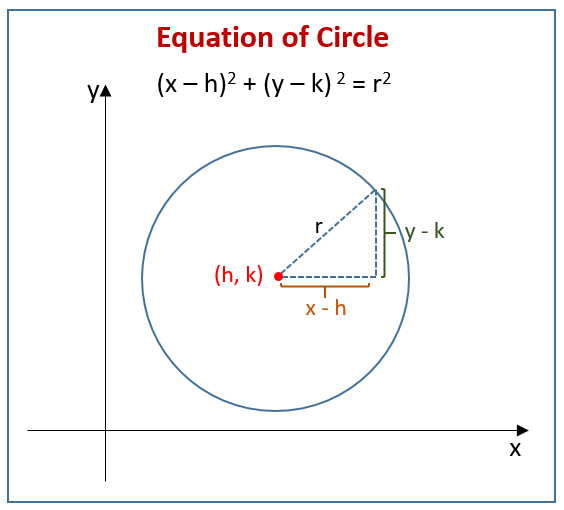
Circle Conic Section
When working with circle conic sections, we can derive the equation of a circle by using coordinates and the distance formula.
The equation of a circle is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 where r is equal to the radius, and the coordinates (x,y) are equal to the circle center.
The variables h and k represent horizontal or vertical shifts in the circle graph.
Examples:
1. Find the center and the radius
a) x2 + (y + 2)2 = 121
b) (x + 5)2 + (y - 10)2 = 9
2. Find the equation the circle with
a) center(-11, -8) and radius 4
b) center (2, -5) and point on circle(-7, -1)
How To Graph A Circle In Standard Form And General Form?
Identify the equation of a circle.
Write the standard form of a circle from general form.
Graph a circle.
A circle is the set of points (x,y) which are a fixed distance r, the radius, away from a fixed point (h,k), the center.
(x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2
Examples:
1. Graph the circle
a) (x - 3)2 + (y + 2)2 = 16
b) x2 + (y - 1)2 = 4
2. Write in standard form and then graph
2x2 + 2y2 - 12x + 8y - 24 = 0
Conic Sections
Introduction to Circles
Understand the equation of a circle
Graph And Write Equations Of Circles
Example:
Graph the equation
(x - 1)2 + (y + 2)2 = 9
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.