Angle between Two Lines
Related Topics:
More Lessons for High School Regents Exam
Math Worksheets
The angle between two lines refers to the acute angle formed at their intersection. If the lines are not parallel or identical, they will form two pairs of vertical angles. We typically refer to the smaller (acute) angle.
The following diagram gives the formula to find the angle between two lines. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
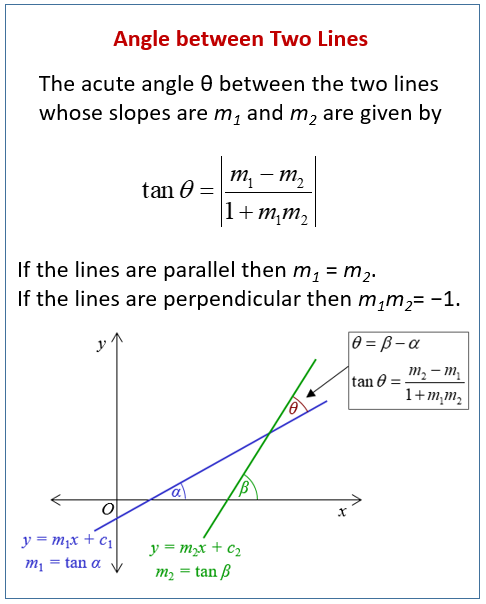
Angle Between Two Lines in 2D (Using Slopes)
If the lines are given in the form y = m1x + c1 and y = m2x + c2, where m1 and m2 are their slopes.
The angle θ between two lines with slopes m1 and m2 is given by:
\(tan\theta=\left|\frac{m_{1}-m_{2}}{1+m_{1}m_{2}}\right|\)
Then,
\(\theta=arctan\left|\frac{m_{1}-m_{2}}{1+m_{1}m_{2}}\right|\)
Note: This formula applies when 1 + m1m2 ≠ 0. If 1 + m1m2 = 0 (i.e. m1m2 = -1), the lines are perpendicular, and θ = 90° or \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
How to find the angle between two straight lines?
Examples:
- Find the acute angle between y = 2x + 1 and y = -3x - 2 to the nearest degree.
- Find the acute angle between 3x - 2y + 7 = 0 and 2y + 4x - 3 = 0 to the nearest degree.
- Find the acute angle between y = x + 3 and y = -3x + 5 to the nearest degree.
Finding Angle Between 2 Lines
How to find the angle between two lines using the formula?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.