Circle Theorems - Alternate Segment Theorem
Related Topics: More Geometry Lessons
Circles have many interesting geometric properties.
In this lesson, we will learn
- a Circle Theorem called The Alternate Segment Theorem.
- how to use the alternate segment theorem.
- how to prove the alternate segment theorem.
What is the Alternate Segment Theorem?
The Alternate Segment Theorem is a fundamental theorem in circle geometry. It establishes a relationship between an angle formed by a tangent and a chord, and an angle within the circle’s “alternate” segment.
Statement of the Alternate Segment Theorem
The Alternate Segment theorem states:
For any circle, an angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.
Key Components:
Tangent: A line that touches the circle at exactly one point (point of contact).
Chord: A line segment joining two points on the circumference.
Alternate Segment: The segment of the circle on the opposite side of the chord from the tangent.
In the following diagram, the chord CE divides the circle into 2 segments. Angle CEA and angle CDE are angles in alternate segments because they are in opposite segments.

The alternate segment theorem states that an angle between a tangent and a chord through the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment. In the above diagram, the alternate segment theorem tells us that angle CEA and angle CDE are equal.
The following diagram shows another example of the alternate segment theorem.
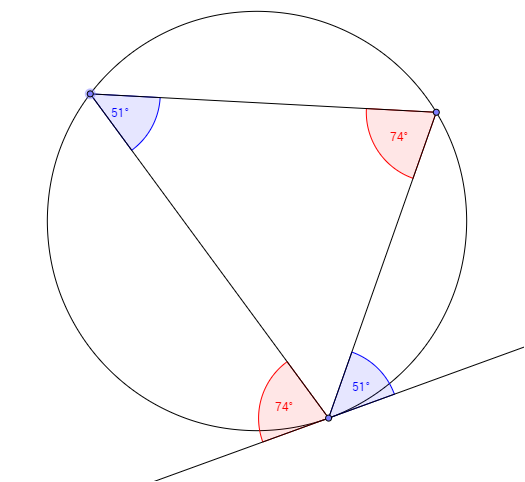
Key Idea:
Angle between Tangent and Chord = Angle in Alternate Segment
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
How to use the Alternate Segment Theorem to find missing angles?
Example:
In the following diagram, MN is a tangent to the circle at the point of contact A. Identify the angle that is equal to x

Solution:
We need to find the angle that is in alternate segment to x.
x is the angle between the tangent MN and the chord AB.
We look at the chord AB and find that it subtends angle ACB in the opposite segment.

So, angle ACB is equal to x.
How to identify the angles that are equal for the alternate segment theorem?
The angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.
Circle Theorem Exam Question
How to solve an exam question that uses the Alternate Segment Theorem and properties of a Tangent?
How to identify angles in the Circle theorems and the Alternate Segment Theorem?
(Maths GCSE Revision)
How to prove the Alternate Segment Theorem?
Draw 3 radii from the center of the circle to the 3 points on the circle to form 3 isosceles triangles.
This video will show how to prove the alternate segment theorem.
Proof of the Alternate Segment Theorem in Circle Theorems
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.