Algebra
This lesson is part of a series of lessons for the quantitative reasoning section of the GRE revised General Test. In this lesson, we will learn:
- Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Combine Like Terms
- Distributive Property
- Factor out the GCF
- Multiplying Expressions
- Expanding
- Perfect Square Trinomials
- Difference of Two Squares
- Simplifying Rational Expressions
Algebra
A variable is a symbol, usually a letter, which is used to represent an unknown number.
A term can be a number, a variable, or a number and variable combined by multiplication or division. Some examples of terms are:
x, 8, 4y, ![]()
An algebraic expression has one or more variables and can be written as a single term or as a sum of terms. Here are some examples of algebraic expressions.
6x, 3w – 8, 3wt + 7t2 + 5t2 – 6, ![]()
In the examples above, 6x is a single term, 3w – 8 has two terms, 3wt + 7t2 + 5t2 – 6 has four terms, and ![]() has one term.
has one term.
In the expression, 3wt + 7t2 + 5t2 – 6, the terms 7t2 and 5t2 are called like terms because they have the same variables, and the corresponding variables have the same exponents. A term that has no variable is called a constant term.
A number that is multiplied by variables is called the coefficient of a term. For example, in the expression 3w + 7t2– 6, 3 is the coefficient of the term 3w, 7 is the coefficient of the term 7t2 and – 6 is a constant term.
The coefficient of 1 in an algebraic term is usually not written. For example, 1y can be written as simply y. So, 1y and y are the same.
This video will help you to understand the terminology for working with algebraic expressions.
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Combine Like Terms
The same rules that govern operations with numbers apply to operations with algebraic expressions. One additional rule, which helps in simplifying algebraic expressions, is that like terms can be combined by adding or subtracting their coefficients.
Example:
a) 14x + 5x = (14 + 5)x = 19x
b) 5y2 – 13y2 + xy = (5 – 13)y2 + xy = –8y2 + xy
c) pr – 2x – 3pr – 5x = (1 – 3)pr + (–2 – 5)x = – 2pr + –7x = –2pr – 7x
Distributive Property
Distributive property allows you to remove the parenthesis (or brackets) in an expression. Multiply the value outside the brackets with each of the terms in the brackets.
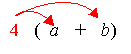
For example:
4(a + b) = 4a + 4b
7(2c – 3d + 5) = 14c – 21d + 35
The following videos show how to simplify algebraic expressions using the distributive property and combining like terms.
Factor out the GCF
A number or variable that is a factor of each term in an algebraic expression can be factored out. We will try to factor out the greatest common factor (GCF).
Example:
a) ad + dc + df = d(a + c + f) ← GCF is d
b) 2pq + 6p2q – 4p3q = 2pq(1 + 3p – 2p2) ← GCF is 2pq
The following video shows how to factor the GCF from an algebraic expression.
Multiplying Expressions
Next, we will consider the multiplication of two algebraic expressions:
(a + b)(c + d)
Such an operation is called ‘expanding the expression’. To expand the expression, we multiply each term in the first pair of brackets by every term in the second pair of brackets.
Example:
a) (y – 3)(2y + 5)
= y(2y+ 5) – 3(2y + 5)
= (y × 2y) + (y × 5) + (–3 × 2y) + (–3 × 5)
= 2y2 + 5y – 6y – 15
= 2y2 – y – 15
b) (a + b)2
= (a + b)(a + b) = a(a + b) + b(a + b)
= a2 + ab + ab + b2
= a2 + 2ab + b2
Here are some common expansions that you will find useful to remember:
(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
(a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
(a + b)(a – b) = a2 – b2
A statement of equality between two algebraic expressions that is true for all possible values of the variables involved is called an identity. All of the statements above are identities. All of the identities above can be used to factorize and simplify algebraic expressions.
The following video shows how to factorize perfect square trinomials: a2 + 2ab* + b2 = (a + b)2, a2 – 2ab + b2 = (a – b)2
The following video shows how to factorize the difference of two squares a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b)
Simplifying Rational Expressions
A rational expression is a fraction in which the numerator and/or the denominator are polynomials.
A rational expression has been simplified or reduced to lowest terms if all common factors from the numerator and denominator have been canceled. So, we first need to factor the polynomials and then cancel any common factors from the top and bottom of the rational expression.
Example:
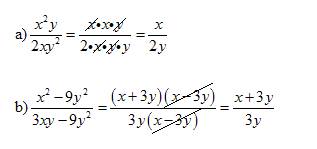
This video explains how to simplify rational expressions.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.