Fractions
Related Pages
Understanding Fractions
Fractions Worksheet
A fraction describes a part of a whole. Fractions appear a lot in everyday life. This lesson will help you understand how to talk about them, how to perform computations with them, how to express them as decimals, and how to distinguish different types of fractions.
What is a Fraction
A fraction consists of two main parts, separated by a horizontal line (called the fraction bar or vinculum):
Numerator (Top Number): The number above the fraction bar. It tells you how many parts of the whole you have or are considering.
Denominator (Bottom Number): The number below the fraction bar. It tells you the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into. The denominator cannot be zero.
Example: In the fraction \(\frac{5}{12}\):
5 is the numerator.
12 is the denominator.
This fraction means “5 out of 12 equal parts of a whole."
Check out this lesson to learn more about the components of a fraction:
Components of a Fraction
Types of Fractions
- Proper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator. Its value is always less than 1.
Examples: \(\frac{1}{2},\frac{3}{4},\frac{7}{10}\) - Improper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Its value is always 1 or greater than 1.
Examples: \(\frac{5}{3},\frac{7}{2},\frac{4}{4}\) - Mixed Number: A combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. Improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers, and vice versa.
Examples: \(1\frac{1}{2}=\frac{3}{2},2\frac{3}{4}=\frac{11}{4}\) - Unit Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is 1.
Examples: \(\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{5},\frac{1}{120}\) - Equivalent Fractions: Fractions that represent the same value, even though they have different numerators and denominators.
Examples: \(\frac{1}{2},\frac{2}{4},\frac{3}{6}\) are all equivalent. You can get equivalent fractions by multiplying or dividing the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number.
Check out this lesson on types of fractions and how to convert between them:
Types of Fractions
Check out this lesson on equivalent fractions:
Equivalent Fractions
Check out this lesson on how to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions:
Mixed Numbers & Improper Fractions
Check out this lesson on how to convert between fractions and decimals:
Fractions & Decimals
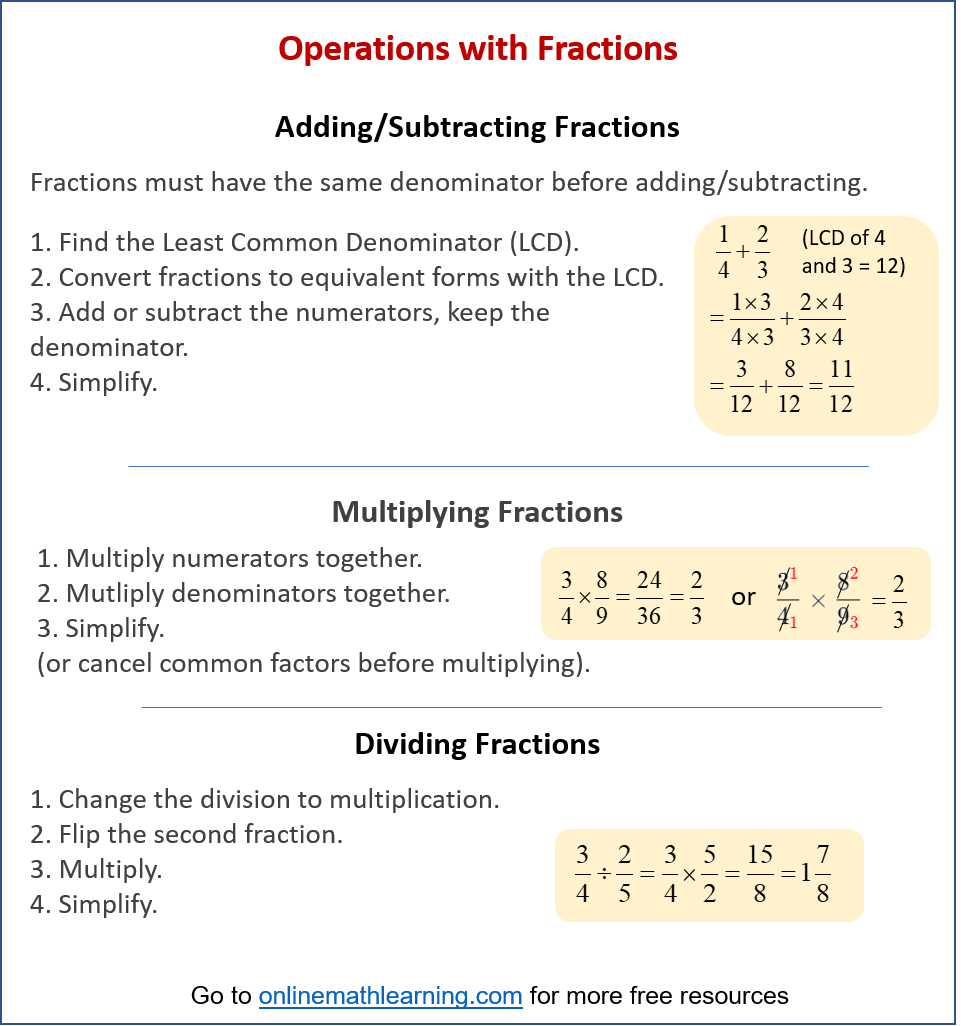
Operations with Fractions
The following diagram shows the operations with fractions: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
Fraction Worksheets
Practice your Fractions with the following worksheets.
Printable & Online Fractions Worksheets
1. Simplifying (Reducing) Fractions
To simplify a fraction, divide both the numerator and the denominator by their common factor. Continue until the only common factor is 1.
Example: Simplify \(\frac{12}{18}\)
\(\frac{12÷6}{18÷6}=\frac{2}{3}\)
2. Adding and Subtracting Fractions
a) If the denominators are different, find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators to create a common denominator.
b) Convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with the common denominator.
c) Add or subtract the numerators, keeping the common denominator.
d) Simplify the resulting fraction if possible.
3. Multiplying Fractions
a) Multiply the numerators together.
b) Multiply the denominators together.
c) Simplify the resulting fraction if possible. (You can often “cross-cancel” before multiplying to make simplification easier).
4. Dividing Fractions
a) Keep the first fraction as it is. Change the division sign to a multiplication sign. Flip (find the reciprocal of) the second fraction.
b) Multiply the fractions as usual.
c) Simplify the result.
Check out these lessons on adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions:
Adding Fractions
Subtracting Fractions
Multiplying Fractions
Dividing Fractions
Videos
What are fractions?
How to Add, Subtract, Multiply, and Divide Fractions?
How to convert fractions to decimals?
Rational Numbers and Fractions
A rational number is a number that can be represented by a fraction whose numerator and denominator are both integers (and the denominator must not be zero), for example: \(\frac{1}{4}, -\frac{3}{5}\).
Since all integers can be written as fractions, so all integers are also rational numbers, for example: \(5 =\frac{5}{1}\)
Some rational numbers may not be so obvious, for example: 0.25 is rational because 0.25 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
\(0.\overline{6}\) is rational because \(0.\overline{6}=\frac{2}{3}\)
\(\sqrt{4}\) is rational because \(\sqrt{4}=2\)
However, \(\sqrt{5}\) is not rational.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.