

Informal Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
Related Topics:
Lesson Plans and Worksheets for Grade 8
Lesson Plans and Worksheets for all Grades
More Lessons for Grade 8
Common Core For Grade 8
Examples, videos, and solutions to help Grade 8 students learn the Pythagorean theorem and an informal proof of the theorem.
Lesson 15 Summary
Given a right triangle ABC with being the vertex of the right angle, then the sides AC and BC are called the legs of △ ABC and AB is called the hypotenuse of △ ABC. Take note of the fact that side a is opposite the angle A, side b is opposite the angle B, and side c is opposite the angle C. The Pythagorean theorem states that for any right triangle, a2 + b2 = c2.
Classwork
Concept Development
The Pythagorean theorem is a famous theorem that will be used throughout much of high school mathematics. For that reason, you will see several proofs of the theorem throughout the year and have plenty of practice using it. The first thing you need to know about the Pythagorean theorem is what it states:
Pythagorean theorem: If the lengths of the legs of a right triangle are a and b, and the length of the hypotenuse is c, then a2 + b2 = c2.
Given a right triangle ABC with C being the vertex of the right angle, then the sides AC and BC are called the legs of △ ABC and AB is called the hypotenuse of △ ABC.
Discussion
The first proof of the Pythagorean theorem that you will see requires you to know some basic facts about geometry:
1. Congruent triangles have equal areas.
2. Triangles can be considered congruent using the Side-Angle-Side Criterion (SAS).
3. The triangle sum theorem. (∠ sum of △)
a. All corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent.
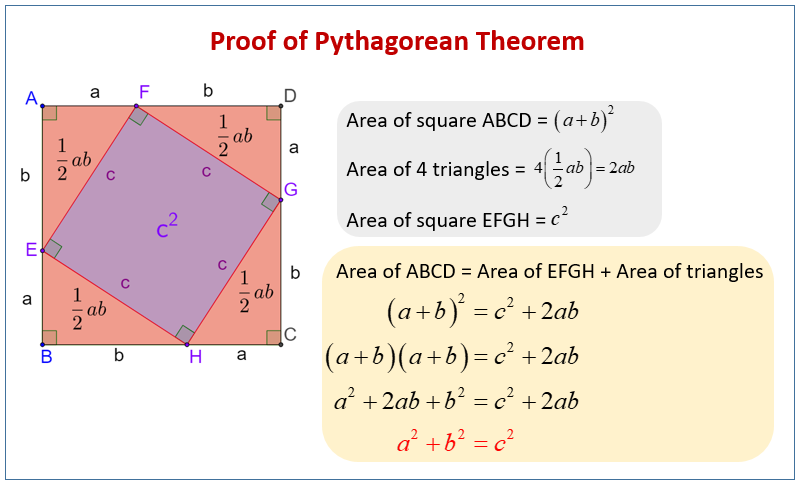
a. For right triangles, the two angles that are not the right angle have a sum of 90°. (∠ sum of △) The following diagram shows a proof for the Pythagorean Theorem. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the Pythagorean Theorem.
Example 1
Now that we know what the Pythagorean theorem is, let’s practice using it to find the length of a hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Example 2
Determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Exercises 1–5
For each of the exercises, determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle shown. Note: Figures not drawn to scale.


Lesson Plans and Worksheets for Grade 8
Lesson Plans and Worksheets for all Grades
More Lessons for Grade 8
Common Core For Grade 8
Examples, videos, and solutions to help Grade 8 students learn the Pythagorean theorem and an informal proof of the theorem.
New York State Common Core Math Module 2, Grade 8, Lesson 15
Worksheets for Grade 8Lesson 15 Student Outcomes
• Students will know the Pythagorean theorem and be shown an informal proof of the theorem.
• Students will use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Lesson 15 Summary
Given a right triangle ABC with being the vertex of the right angle, then the sides AC and BC are called the legs of △ ABC and AB is called the hypotenuse of △ ABC. Take note of the fact that side a is opposite the angle A, side b is opposite the angle B, and side c is opposite the angle C. The Pythagorean theorem states that for any right triangle, a2 + b2 = c2.
Classwork
Concept Development
The Pythagorean theorem is a famous theorem that will be used throughout much of high school mathematics. For that reason, you will see several proofs of the theorem throughout the year and have plenty of practice using it. The first thing you need to know about the Pythagorean theorem is what it states:
Pythagorean theorem: If the lengths of the legs of a right triangle are a and b, and the length of the hypotenuse is c, then a2 + b2 = c2.
Given a right triangle ABC with C being the vertex of the right angle, then the sides AC and BC are called the legs of △ ABC and AB is called the hypotenuse of △ ABC.
Discussion
The first proof of the Pythagorean theorem that you will see requires you to know some basic facts about geometry:
1. Congruent triangles have equal areas.
2. Triangles can be considered congruent using the Side-Angle-Side Criterion (SAS).
3. The triangle sum theorem. (∠ sum of △)
a. All corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent.
a. For right triangles, the two angles that are not the right angle have a sum of 90°. (∠ sum of △) The following diagram shows a proof for the Pythagorean Theorem. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the Pythagorean Theorem.
Now that we know what the Pythagorean theorem is, let’s practice using it to find the length of a hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Example 2
Determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Exercises 1–5
For each of the exercises, determine the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle shown. Note: Figures not drawn to scale.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.