Permutations & Combinations (IGCSE Worked Examples)
Related Pages
GCSE/IGCSE Math Past Papers
Math Worksheets
In these lessons, we will look at worked examples of problems on Permutations & Combinations as typically found in IGCSE Additional Maths.
The following figure gives the formula for Permutations and Combinations. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions on how to use the formulas to solve examination word problems.
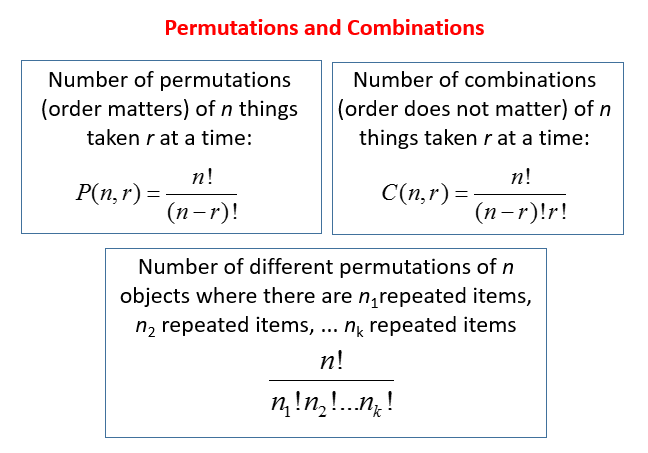
IGCSE Add Maths - Permutations & Combinations
Learn how to recognise between a permutation case and a combination case. How to deal with repetitions, restrictions and complements?
-
(i) Find the number of different arrangements of the letters of the word MEXICO
Find the number of these arrangements
(ii) which begin with M,
(iii) which have the letter X at one end and the letter C at the other end. -
A garden centre sells 10 different varieties of rose bush. A gardener wishes to buy 6 rose bushes, all of different varieties.
(i) Calculate the number of ways she can make her selection.
Of the 10 varieties, 3 are pink, 5 are red and 2 are yellow. Calculate the number of ways in which her selection of 6 rose bushes could contain
(ii) no pink rose bush,
(iii) at least one rose bush of each colour. -
(a) An examination paper contains 12 different questions of which 3 are on trigonometry, 4 are on algebra and 5 are on calculus. Candidates are asked to answer 8 questions. Calculate
(i) the number of different ways in which a candidate can select 8 questions if there is no restriction.
(ii) the number of these selections which contain questions on only 2 of the 3 topics, trigonometry, algebra and calculus.
(b) A fashion magazine runs a competition, in which 8 photographs of dresses are shown, lettered A,B,C,D,D,F,G and H. Competitors are asked to submit an arrangement of 5 letters showing their choice of dresses in descending order of merit. The winner is picked at random from those competitiors whose arrangement of letters agrees with that chosen by a panel of experts.
(i) Calculate the number of possible arrangements of 5 letters chosen from the 8.Br> Calculate the number of these arrangements
(ii) in which A is placed first,
(iii) which contain A.
0606 S12 Paper 11 Question 4
CIE IGCSE syllabus 0606 (and also CIE GCE O-Level syllabus 4037) - Additional Mathematics Paper 1 May/June 2012. Additional Maths Paper 1 May/June 2012 (pdf)
a) Arrangements containing 5 different letters from the word AMPLITUDE are to be made.
Find
i) the number of 5-letter arrangements if there are no restrictions,
ii) the number of 5-letter arrangements which start with the letter A and end with the letter E.
b) Tickets for a concert are given out randomly to a class containing 20 students. No student is given more than one ticket. There are 15 tickets.
i) Find the number of ways in which this can be done.
There are 12 boys and 8 girls in the class. Find the number of different ways in which
ii) 10 boys and 5 girls get tickets,
iii) all the boys get tickets.
Solution:
a)
i) Since there are 9 different letters, and we pick 5 to be arranged, there are 9P5 = 15,120 permutations.
ii) Since A and E are fixed, there are only 3 other letters to arrange in between them, from the remaining 7 letters (9 letters minus the A and E).
∴ there are 7P3 = 210 permutations.
b)
i) This means selecting 15 students from 20, so we have 20C15 = 15,504 ways.
ii) Selecting 10 boys from 12, we have 12C10 = 66 ways.
Selecting 5 girls from 8, we have 8C5 = 56 ways.
∴ the total is 12C10 × 8C5 = 3,696 ways.
iii) All 12 boys got tickets, so there is only 1 way to select all the boys.
The remaining 3 tickets go to 3 girls from 8, we have 8C3 = 56 ways.
∴ the total is 8C3 × 1 = 56 ways.
0606 W12 Paper 21 Question 9
a) An art gallery displays 10 paintings in a row. Of these paintings, 5 are by Picasso, 4 by Monet and 1 by Turner.
i) Find the number of different ways the paintings can be displayed if there are no restrictions.
ii) Find the number of different ways the paintings can be displayed if the paintings by each of the artists are kept together.
b) A committee of 4 senior students and 2 junior students is to be selected from a group of 6 senior students and 5 junior students.
i) Calculate the number of different committees which can be selected.
One of the 6 senior students is a cousin of one of the 5 junior students.
ii) Calculate the number of different committees which can be selected if at most one of these cousins is included.
Solution:
a)
i) Since there are 10 different items to be arranged, there are 10! = 3,628,800 permutations.
ii) Picasso’s paintings can be arranged in 5! ways,
Monet’s can be arranged in 4! ways and
Turner’s can be arranged in 1! = 1 way.
Also, the 3 artists can be arranged in 3! ways (P-M-T, P-T-M, M-T-P, etc)
∴ the total is 5! × 4! × 3! = 17,280 permutations.
b)
i) Selecting 4 seniors from 6, we have 6C4 = 15 selections.
Selecting 2 juniors from 5, we have 5C2 = 10 selections.
∴ the total is 6C4 × 5C2 = 150 selections.
ii) “At most one” means that there may be none of the cousins, or only one of the cousins included. So we can work out all the different scenarios: none of the cousins, only the senior cousin included, or only the junior cousin included and add all the selections.
An alternative is to work out the number of selections where both cousins are in; then we subtract from the total (from b(i) above) and the remaining selections would have at most one of the cousins.
If both cousins are included, then we select only 3 other seniors from the remaining 6, and 1 other junior from the remaining 4.
So, there are 5C3 × 4C1 = 40 selections where both cousins are included.
∴ there are 150 − 40 = 110 selections where there is at most one of the cousins.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.