Group 1 Elements - Alkali Metals
Related Topics:
More Lessons for IGCSE Chemistry
Math Worksheets
A series of free IGCSE Chemistry Activities and Experiments (Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry).
Group 1 Alkali Metals
Hardness of Alkali Metals
The alkali metals are very soft. Lithium is the hardest alkali metal and they become softer as you go down the group.
Alkali metals reacting with chlorine
All of the alkali metals react vigorously with chlorine gas. Each reaction produces a white crystalline salt. The reaction gets more violent as you move down Group 1, showing how reactivity increases down the group.
Alkali metals reacting with water
All alkali metals react vigorously with cold water. In each reaction, hydrogen gas is given off and the metal hydroxide is produced. The speed and violence of the reaction increases as you go down the group. This shows that the reactivity of the alkali metals increases as you go down group 1.
Why does the reactivity increase down the group?
All alkali metals have one electron in the outer shell. In a reaction, this electron is lost and the alkali metal forms a +1 ion. As you go down group 1, the number of electron shells increases – lithium has two, sodium has three etc. Therefore, the outermost electron gets further from the nucleus. The attraction from the positive nucleus to the negative electron is less. This makes it easier to remove the electron and makes the atom more reactive.
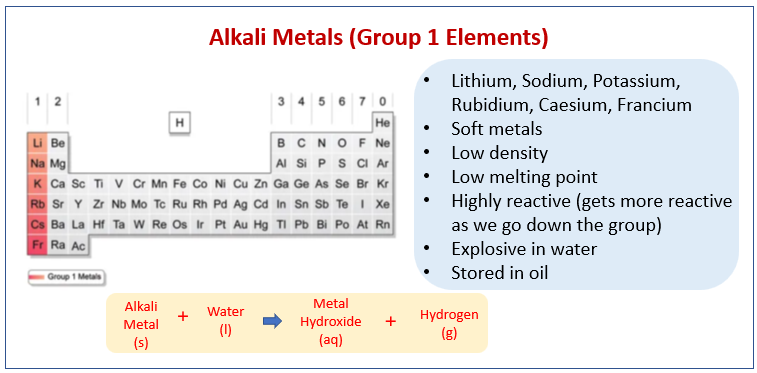
The following diagram shows the Alkali Metals (Group 1 Elements) and their properties. Scroll down the page for more examples and explanations.
The following video will:
- Describe the shared Properties of Group 1 Alkali Metals
- Compare the reactions of alkali metal in water
- Explain why the alkali metals become more reactive down the group
The following chemistry demonstration video shows the reactions of group 1 metals (lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K)) in air, in chlorine and in water.
Questions
- Explain why the alkali metals become more reactive down the group.
- Record your following observations for lithium, sodium and potassium:
Physical properties, Heating in air, Heating in Chlorine, Reaction with water. - Write the word equation and symbol equation for each reaction.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.